Cheddar cheese is one of the most popular cheeses, but it is also among the highest in cholesterol and
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
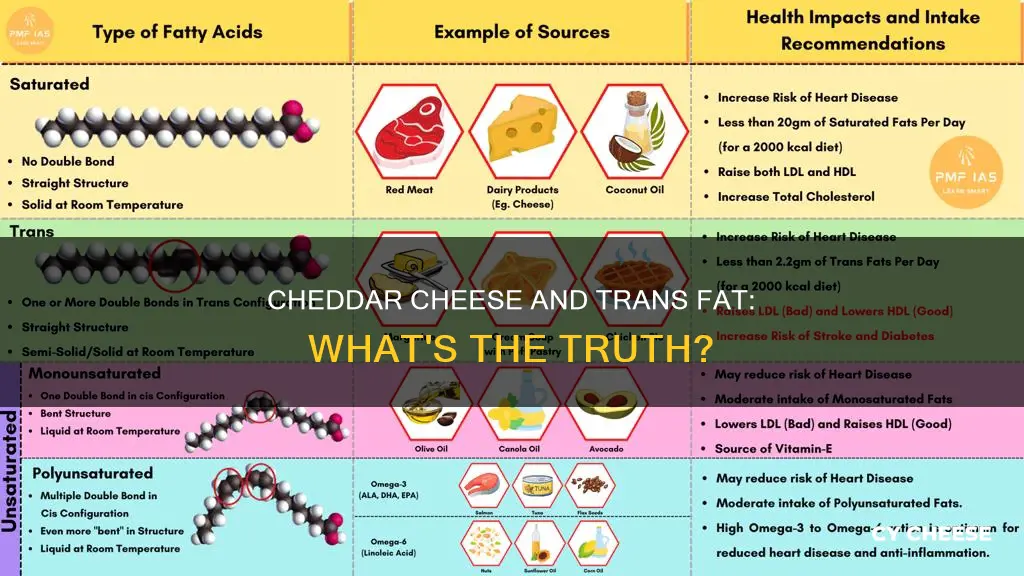
| Does cheddar cheese contain trans fat? | While cheddar cheese contains saturated fat, it does not contain trans fat. However, it may contain some naturally occurring trans fats. |
| How much is considered a serving of cheddar cheese? | A serving of cheddar cheese is about 40 grams or the size of a matchbox. |
| What are the nutritional benefits of cheddar cheese? | Cheddar cheese is rich in protein, calcium, and vitamin B12. It also contains other vitamins and minerals. |
| What are the concerns about consuming cheddar cheese? | Cheddar cheese is high in saturated fat, which is linked to an increased risk of high LDL cholesterol, heart disease, and stroke. |
| How can one consume cheddar cheese as part of a healthy diet? | It is recommended to choose low-fat or reduced-fat versions of cheddar cheese, which have lower amounts of saturated fat. Consuming cheese in moderation, as part of a healthy, well-balanced diet, is generally considered acceptable. |
Explore related products
$15.85 $17.25
$1.74
What You'll Learn
- Cheddar cheese is high in cholesterol and saturated fat
- It is also a good source of protein and calcium
- Cheddar may contain some naturally occurring trans fats
- Lower-fat varieties of cheddar cheese reduce total fat and trans fat intake
- Nutritionists say cheese can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation

Cheddar cheese is high in cholesterol and saturated fat
Cheddar cheese is a popular variety of cheese, often consumed in sandwiches, grated on pasta, or as part of a wine-and-cheese platter. While it is a good source of protein and calcium, it is also high in cholesterol and saturated fat.
A 40-gram serving of cheddar cheese contains about 500-650 kJ of energy, and is considered one of the recommended two to three servings of dairy per day. However, due to its high saturated fat content, it is recommended to consume cheddar cheese in moderation. Saturated fat is known to increase the risk of high LDL cholesterol, heart disease, and stroke. Therefore, it is advisable to opt for low-fat or fat-free versions of cheddar cheese, which have significantly less saturated fat and cholesterol. These versions can be easily found in supermarkets and provide a healthier alternative without compromising on taste.
In addition to choosing lower-fat varieties, portion control is another effective way to reduce saturated fat and cholesterol intake. Instead of using three slices of cheese on a sandwich, one slice can suffice. Alternatively, grated cheese can be used, as it covers more surface area and gives the impression of a larger portion. Hard and "stinky" cheeses, such as aged Parmesan or Asiago, can also be grated in small amounts to add a burst of flavor to pasta dishes.
While some sources suggest that cheese is neutral in terms of its impact on health, others recommend consulting a doctor if one is trying to lose weight or has existing heart disease. Overall, the key to including cheddar cheese in one's diet is moderation. By being mindful of portion sizes and opting for lower-fat varieties, individuals can still enjoy the taste and nutritional benefits of cheddar cheese while maintaining a balanced and healthy diet.
Cheddar Cheese's Rotten Egg Smell: Why?
You may want to see also

It is also a good source of protein and calcium
Cheddar cheese is a good source of protein and calcium. While it may contain some naturally occurring trans fats, choosing lower-fat cheese varieties can reduce the amount of trans fat in your diet.
Protein is one of the body's key building blocks, essential for the growth, renewal, and healing of cells, tissues, and organs. It also plays a vital role in supporting healthy weight management by reducing appetite and managing hunger levels. Research suggests that a higher protein intake may be beneficial for maintaining bone mass and lowering the risk of osteoporosis, especially when combined with resistance training. Furthermore, increasing protein intake can contribute to building lean muscle mass by aiding muscle recovery, repair, and regrowth.
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body, with 99% of it found in bones and teeth. It is crucial for bone development, growth, and maintenance, helping to slow down bone density loss, which is a natural part of ageing. Calcium also plays a key role in blood clotting, muscle contraction, and cardiovascular function. Additionally, it is necessary for maintaining healthy communication between the brain and other parts of the body.
Both calcium and protein are essential nutrients for overall health and well-being. While supplements are available, it is generally recommended to obtain these nutrients from natural food sources whenever possible.
Cheddar Cheese: Soft or Hard?
You may want to see also

Cheddar may contain some naturally occurring trans fats
Cheddar cheese is one of the most popular cheeses and is consumed by one-third of Australians. It is also one of the most ancient foods for humans and has been a part of our diet for several thousand years. Cheddar is a hard cheese, and a serve is about 40g.
Cheddar cheese is rich in proteins and fat, which provide important building blocks (amino acids and fatty acids) for our body. It also contains many other important ingredients, including vitamins and minerals, all of which are needed to maintain good health.
While cheddar cheese can be a part of a healthy, well-balanced diet, it is important to choose the right types and consume it in moderation. Cheddar cheese is among the highest in cholesterol and saturated fat. Therefore, opting for low-fat or fat-free versions of cheddar cheese can be a healthier option, as they contain far less saturated fat and cholesterol than their whole-fat counterparts.
Cheddar Cheese Sharpness: Does Color Play a Role?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Lower-fat varieties of cheddar cheese reduce total fat and trans fat intake
Cheddar cheese is one of the most popular cheeses, but it is also among the highest in cholesterol and saturated fat. A 4-ounce serving of full-fat cheddar contains 81 calories, 1 gram of fat, and 14 grams of protein.
However, several fat-free and low-fat versions of cheddar are widely available in supermarkets. These include non-fat and low-fat cheddars, which contain no more than 1 gram of saturated fat per serving. Reduced-fat cheddar is one of the lowest-fat cheeses available on the market. A 4-ounce serving of low-fat cheddar contains only 2 grams of total fat and 1 gram of saturated fat, while still providing 14 grams of protein.
Lower-fat varieties of cheddar cheese can help reduce total fat and trans-fat intake. According to the NZFSA, choosing lower-fat varieties of milk and milk products reduces the amount of total fat and trans fat consumed. This is because the lower the fat content, the lower the amount of trans fat present.
In addition to reducing total fat and trans-fat intake, lower-fat varieties of cheddar cheese can also help with weight loss. A strong, sharp cheddar can add flavour to dishes without adding too many calories, as a smaller portion can be used.
The Cheddar Conundrum: Finding the Finest Aged Cheese
You may want to see also

Nutritionists say cheese can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation
Nutritionists agree that cheese can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. Cheese is a good source of calcium, protein, vitamins A and B12, zinc, phosphorus, and riboflavin. It also contains beneficial bacteria or yeast that contribute to a healthy microbiome.
However, it's important to note that cheese is also high in calories, saturated fat, and sodium, which can increase the risk of heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular problems if consumed in excess. Therefore, it's recommended to choose lower-fat varieties of cheese and to stick to moderate portions, such as the serving size of 40 grams or about the size of a matchbox.
Cheddar cheese, a popular variety, is a good example of a cheese that can be part of a healthy diet in moderation. It is a fermented cheese that offers consistent benefits for bone health due to its high protein, calcium, and vitamin D content. Additionally, aged cheddar has a lower lactose content, making it a better option for those with lactose intolerance.
When choosing cheese, it's important to consider the other foods you will be pairing it with. For example, if you're usually eating cheese with processed foods like pizza crust, pepperoni, or crackers, you might be cancelling out the benefits. Checking the nutrition facts label can help you make an informed choice, allowing you to pick the cheese with the most calcium and the least sodium and saturated fat.
The Real Deal: Schuler's Cheddar Cheese Spread and Pasteurization
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Cheddar cheese contains saturated fat, which is different from trans fat. Trans fat is an industrial product, whereas saturated fat is naturally occurring in dairy products.
The Australian Guide to Healthy Eating recommends two to three servings of dairy per day, or four servings for women over 50. A serving is about 40 grams, or the size of a matchbox.
Cheese is a good source of protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals. It is also a fermented food, which contributes to a healthy microbiome.
Cheese contains salt and saturated fat, which can increase the risk of high LDL cholesterol, heart disease, and stroke. However, low-fat and fat-free cheeses are widely available and can be a healthier alternative.
When adding cheese to a dish, use a measuring cup or spoon instead of portioning by hand. Opt for low-fat or fat-free cheeses, and consider swapping high-fat cheeses for cottage cheese or ricotta.











































