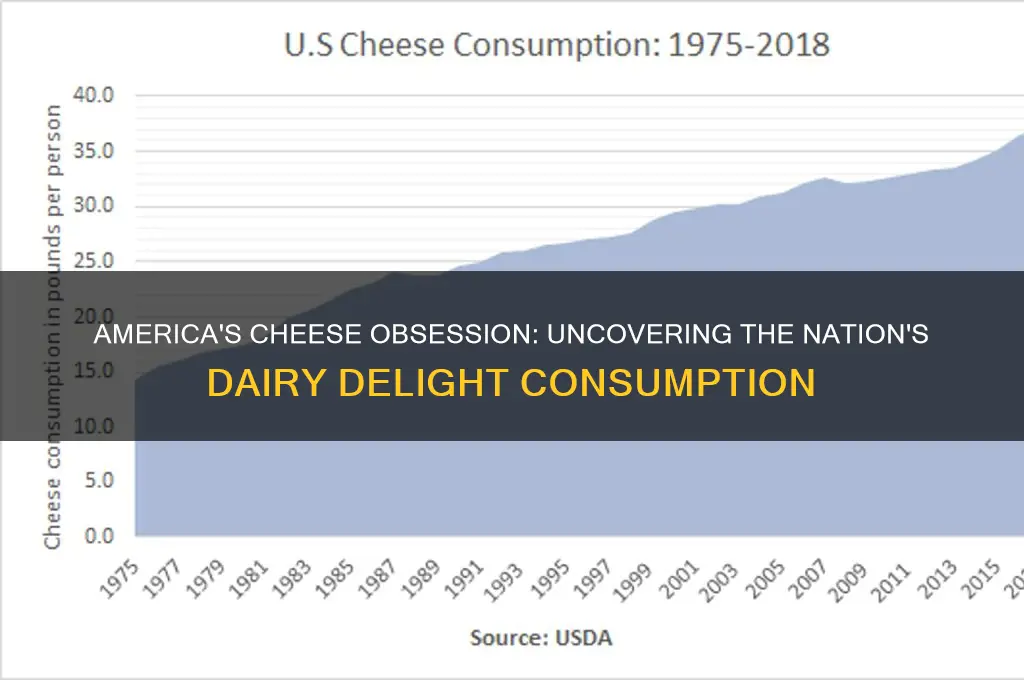
America's love affair with cheese is undeniable, with the average American consuming approximately 40 pounds of cheese per year, a figure that has more than tripled since the 1970s. This staggering amount translates to billions of pounds of cheese consumed annually across the nation, making the United States one of the largest cheese consumers in the world. From classic cheddar and mozzarella to artisanal varieties like gouda and brie, cheese has become a staple in American diets, featuring prominently in everything from burgers and pizzas to charcuterie boards and gourmet dishes. The country's insatiable appetite for cheese is driven by its versatility, cultural significance, and the thriving dairy industry, which continues to innovate and produce an ever-expanding array of cheese products to meet the demands of cheese enthusiasts nationwide.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Annual Cheese Consumption (2022) | Approximately 38.7 pounds per capita |
| Total Cheese Consumption (2022) | Over 12.6 billion pounds |
| Most Consumed Cheese Type | Mozzarella (primarily used in pizza and pasta dishes) |
| Cheese Consumption Trend (2000-2022) | Increased by about 40% |
| Cheese Production (2022) | Over 13 billion pounds (U.S. is the largest cheese producer globally) |
| Cheese Imports (2022) | Approximately 400 million pounds |
| Cheese Exports (2022) | Approximately 350 million pounds |
| Per Capita Spending on Cheese (2022) | Around $170 annually |
| Popular Cheese Varieties | Cheddar, Mozzarella, Parmesan, American, Swiss, and Provolone |
| Cheese Consumption by Age Group | Highest among adults aged 25-54 |
| Cheese Consumption by Region | Midwest and Northeast regions consume the most cheese |
| Cheese in Dietary Intake | Accounts for about 10% of daily saturated fat intake in the U.S. |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn

Annual Cheese Consumption Trends
The United States is one of the largest consumers of cheese globally, with annual cheese consumption trends reflecting both cultural preferences and economic factors. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), the average American consumes approximately 40 pounds of cheese per year. This figure has been steadily rising over the past few decades, driven by the versatility of cheese in American diets, from pizzas and burgers to snacks and gourmet dishes. The trend highlights a growing appetite for cheese, supported by its integration into everyday meals and the expanding variety of cheese products available in the market.
Economic factors play a significant role in shaping annual cheese consumption trends in the U.S. Fluctuations in dairy prices, influenced by supply chain dynamics and global markets, can impact consumer behavior. For instance, during periods of lower dairy prices, cheese consumption tends to rise as it becomes more affordable for both consumers and foodservice providers. Conversely, higher prices may lead to moderation in consumption or a shift toward more cost-effective cheese alternatives. The dairy industry’s ability to innovate and offer value-added products also influences trends, as convenience-oriented options like pre-shredded cheese and snack packs continue to gain popularity.
Demographic changes and lifestyle trends further contribute to the evolution of annual cheese consumption in America. The growing Hispanic population, for example, has increased demand for cheeses like queso fresco and Oaxaca, which are staples in Latin American cuisine. Similarly, the rise of remote work and home cooking during the COVID-19 pandemic boosted cheese consumption as more meals were prepared at home. However, as lifestyles return to pre-pandemic norms, there is a renewed focus on convenience and on-the-go cheese products, such as cheese sticks and individually packaged portions, which are expected to sustain consumption levels.
Sustainability and ethical considerations are emerging as factors influencing annual cheese consumption trends. Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of dairy production and are seeking out cheeses produced using sustainable practices. Organic and locally sourced cheeses are gaining traction, though they still represent a smaller segment of the market. Additionally, plant-based cheese alternatives are carving out a niche, particularly among vegan and lactose-intolerant consumers. While traditional cheese remains dominant, these trends suggest a gradual diversification of the cheese market to align with broader societal values and dietary preferences.
Carb Content in Swiss Cheese: Unveiling a Slice's Nutritional Secrets
You may want to see also

Popular Cheese Types in America
According to recent data, Americans consume a staggering amount of cheese, with the average person eating around 37 pounds of cheese per year. This love for cheese has led to a diverse range of cheese types gaining popularity across the country. When it comes to Popular Cheese Types in America, several varieties stand out due to their versatility, flavor, and widespread availability.
One of the most beloved cheese types in America is Cheddar. Originating from England, Cheddar has become a staple in American households. Its sharp, tangy flavor and firm texture make it ideal for sandwiches, burgers, and macaroni and cheese. Cheddar is also a favorite for snacking, often paired with crackers or apples. The cheese comes in various ages, from mild to extra sharp, catering to different taste preferences.
Another widely consumed cheese in America is Mozzarella. This Italian cheese is a key ingredient in pizzas and pasta dishes like lasagna and caprese salads. Mozzarella’s mild, milky flavor and stretchy texture make it a crowd-pleaser. It is typically made from cow’s milk, though buffalo mozzarella is also available for those seeking a richer taste. Its versatility and melting properties have cemented its place in American cuisine.
American Cheese, despite its name, is a processed cheese product rather than a traditional cheese. It is incredibly popular due to its meltability and mild flavor, making it a go-to choice for grilled cheese sandwiches, cheeseburgers, and burgers. American cheese slices are a convenience food staple, often found in school lunches and quick meals. While it may not be as artisanal as other cheeses, its affordability and ease of use contribute to its widespread consumption.
Pepper Jack has gained significant popularity in recent years, especially among those who enjoy a bit of heat. This spicy variation of Monterey Jack cheese is infused with chili peppers and spices, adding a kick to dishes like tacos, nachos, and sandwiches. Its semi-soft texture and bold flavor profile appeal to adventurous eaters, making it a favorite in Tex-Mex and Southwestern cuisine.
Lastly, Parmesan holds a special place in American kitchens, particularly as a topping for pasta dishes, salads, and soups. This hard, granular cheese has a nutty, savory flavor that enhances the taste of many recipes. While authentic Parmigiano-Reggiano is highly prized, more affordable Parmesan varieties are widely available, ensuring its accessibility to cheese lovers across the country. Its long shelf life and ability to elevate dishes make it a pantry essential.
In conclusion, the Popular Cheese Types in America reflect the nation’s diverse culinary preferences and the cheese industry’s ability to cater to a wide range of tastes. From the sharpness of Cheddar to the meltiness of Mozzarella, the convenience of American cheese, the spiciness of Pepper Jack, and the richness of Parmesan, these cheeses have become integral to American food culture. As cheese consumption continues to rise, these varieties will likely remain favorites for years to come.
Dairy Content in Skim Mozzarella: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Regional Cheese Consumption Differences
The United States is one of the largest consumers of cheese globally, with Americans enjoying a wide variety of cheese types in their diets. However, cheese consumption is not uniform across the country; significant regional differences exist, influenced by factors such as cultural heritage, local food traditions, and economic conditions. Understanding these regional variations provides insight into how cheese is integrated into American cuisine and lifestyle.
In the Northeast, particularly in states like Wisconsin, New York, and Vermont, cheese consumption is notably high. Wisconsin, often referred to as "America's Dairyland," leads the nation in cheese production and consumption. The region's strong dairy farming tradition and the presence of numerous artisanal cheesemakers contribute to its high per capita cheese intake. New York City, with its diverse population, also boasts a robust cheese culture, driven by specialty shops, restaurants, and a penchant for gourmet cheeses. Vermont, another major dairy state, is famous for its cheddar and other artisanal cheeses, which are widely consumed locally.
The Midwest is another region with high cheese consumption, largely due to its dairy-centric agriculture. States like Minnesota, Iowa, and Illinois have a strong tradition of incorporating cheese into everyday meals, from cheese curds to casseroles. The Midwest's love for comfort food, often featuring cheese as a key ingredient, further boosts consumption. Additionally, the region's proximity to major cheese-producing states like Wisconsin ensures a steady supply of fresh, high-quality cheese.
In contrast, the Southern states generally exhibit lower per capita cheese consumption compared to the Northeast and Midwest. Southern cuisine traditionally emphasizes meats, vegetables, and grains, with cheese playing a less prominent role. However, there are exceptions, such as Texas, where the influence of Mexican cuisine has led to higher consumption of cheeses like cheddar and Monterey Jack, often used in dishes like queso and tacos. The South's growing food scene and increasing cultural diversity are gradually introducing more cheese varieties into the regional diet.
The West Coast, particularly California, stands out for its unique cheese consumption patterns. California is the largest milk-producing state in the U.S. and has a thriving artisanal cheese industry. The region's health-conscious population often opts for specialty cheeses, such as goat cheese, blue cheese, and organic varieties. Additionally, the influence of Hispanic and Asian cuisines in California has led to the incorporation of cheeses like queso fresco and paneer into local diets. The Pacific Northwest, with its focus on farm-to-table dining, also supports a strong artisanal cheese culture, though overall consumption may be lower than in the Midwest or Northeast.
Finally, regional differences in cheese consumption are also shaped by economic factors. Wealthier areas tend to have higher consumption of premium and specialty cheeses, while more affordable, mass-produced cheeses dominate in lower-income regions. Urban areas, with greater access to specialty food stores and restaurants, generally consume a wider variety of cheeses compared to rural areas, where options may be more limited. These regional variations highlight the diverse ways in which cheese is enjoyed across America, reflecting both historical traditions and contemporary culinary trends.
Double Quarter Cheese Plate Price: A Cost Breakdown Guide
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Cheese Consumption vs. Global Averages
The United States stands out as one of the largest consumers of cheese globally, with its per capita consumption significantly surpassing the world average. According to recent data, the average American consumes approximately 40 pounds (18 kilograms) of cheese annually. This figure is nearly double the global average, which hovers around 22 pounds (10 kilograms) per person per year. The disparity highlights America’s deep-rooted love for cheese, driven by cultural preferences, culinary traditions, and the widespread availability of cheese in various forms, from pizza toppings to snack products. This high consumption rate is not only a testament to cheese’s popularity in the U.S. but also raises questions about its economic and health implications compared to global trends.
When comparing cheese consumption in the U.S. to other regions, Europe emerges as a notable point of reference, given its historical association with cheese production and consumption. Countries like France, Germany, and Italy consume cheese at rates similar to or slightly higher than the U.S., often exceeding 50 pounds per capita annually. However, these nations typically consume cheese as part of balanced diets, emphasizing quality and tradition. In contrast, American cheese consumption is often tied to processed and convenience foods, which may contribute to higher intake but differ in nutritional value. Meanwhile, many Asian and African countries consume far less cheese, with per capita averages below 5 pounds annually, due to dietary traditions, economic factors, and cultural preferences for other protein sources.
The economic impact of America’s cheese consumption is substantial, both domestically and globally. The U.S. is not only a major consumer but also a significant producer and exporter of cheese, with the dairy industry contributing billions of dollars to the economy. However, this high consumption level has environmental consequences, as cheese production is resource-intensive, requiring large amounts of milk, water, and land. Globally, countries with lower cheese consumption tend to have smaller environmental footprints in this sector, though their dietary patterns may rely on other resource-intensive foods. This contrast underscores the need for sustainable practices in cheese production and consumption, particularly in high-consuming nations like the U.S.
Health considerations also play a role in the cheese consumption debate. While cheese is a good source of protein, calcium, and vitamins, excessive intake, especially of processed varieties high in sodium and saturated fats, can contribute to health issues such as obesity and cardiovascular diseases. The U.S., with its higher consumption rates, faces greater challenges in balancing the nutritional benefits of cheese with its potential health risks. In comparison, countries with moderate cheese consumption often integrate it into diets that prioritize whole, unprocessed foods, mitigating some of these risks. This difference highlights the importance of dietary context and portion control in cheese consumption.
Finally, cultural and culinary factors significantly influence cheese consumption patterns. In the U.S., cheese is a staple in popular foods like burgers, pizzas, and tacos, making it a ubiquitous part of the American diet. This integration into everyday meals contrasts with global averages, where cheese may be reserved for specific dishes or occasions. Efforts to align U.S. consumption habits with global averages could involve promoting mindful eating, diversifying dietary choices, and encouraging the consumption of cheese in moderation. By understanding these disparities, policymakers, industries, and consumers can work toward more balanced and sustainable cheese consumption practices.
Perfect Cheese-to-Brat Ratio: Mastering the Art of Cheesy Sausage Bliss
You may want to see also

Impact of Cheese on U.S. Economy
The United States is one of the largest consumers of cheese globally, and this high demand has significant implications for the country's economy. According to recent data, Americans consume over 37 pounds of cheese per capita annually, a figure that has been steadily rising over the past few decades. This voracious appetite for cheese drives a multi-billion-dollar industry, creating jobs, stimulating rural economies, and contributing to both domestic and international trade. The cheese industry is deeply intertwined with the U.S. agricultural sector, particularly dairy farming, which forms the backbone of cheese production.
The economic impact of cheese consumption begins at the farm level. Dairy farms across the U.S., especially in states like Wisconsin, California, and Idaho, produce the milk necessary for cheese manufacturing. These farms generate substantial revenue, support local communities, and contribute to the overall GDP. The dairy sector employs hundreds of thousands of workers, from farmers and farmhands to veterinarians and equipment suppliers. As cheese consumption grows, so does the demand for milk, ensuring the sustainability and expansion of dairy operations. This, in turn, strengthens rural economies and reduces urban migration by providing stable livelihoods in agricultural regions.
Cheese production itself is a major economic driver, with the U.S. boasting over 1,200 cheese plants that produce a wide variety of cheeses, from cheddar and mozzarella to artisanal and specialty cheeses. These facilities require significant investment in infrastructure, technology, and labor, further boosting economic activity. The cheese industry also fosters innovation, as companies invest in research and development to create new products, improve production efficiency, and meet evolving consumer preferences. This innovation not only enhances the industry's competitiveness but also positions the U.S. as a global leader in dairy technology.
The retail and food service sectors also benefit immensely from America's love for cheese. Supermarkets, restaurants, pizzerias, and fast-food chains rely heavily on cheese as a key ingredient in their products. For example, the pizza industry alone consumes over 2 billion pounds of cheese annually, highlighting its critical role in food service. Additionally, the export of American cheese contributes to the country's trade balance. The U.S. exports over $600 million worth of cheese annually, with key markets including Mexico, Canada, and Asia. This international trade not only generates revenue but also enhances the global reputation of American dairy products.
Finally, the cheese industry has indirect economic impacts through its supply chain and related industries. Packaging, transportation, marketing, and equipment manufacturing all benefit from the demand for cheese. For instance, the logistics sector plays a vital role in distributing cheese products across the country and overseas, creating additional jobs and business opportunities. Moreover, the tourism industry in cheese-producing regions, such as Wisconsin's "Cheese Country," attracts visitors, further stimulating local economies. In summary, the impact of cheese on the U.S. economy is profound and multifaceted, touching sectors from agriculture to retail and beyond. As consumption continues to rise, the cheese industry will remain a vital component of America's economic landscape.
Uncovering the Fat Content in Farmer Boys' Chili Cheese Fries
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
America consumes approximately 37.5 pounds of cheese per person annually, totaling over 12 billion pounds nationwide.
Mozzarella is the most popular cheese in the U.S., largely due to its use in pizza and pasta dishes.
Yes, cheese consumption in the U.S. has steadily increased over the past few decades, rising from about 10 pounds per person in the 1970s to over 37 pounds today.
Wisconsin is often considered the top cheese-consuming state per capita, given its strong dairy industry and cheese culture.
The U.S. is one of the largest cheese consumers globally, though countries like France and Germany have higher per capita consumption, averaging around 50-60 pounds per person annually.











































