Blue cheese, renowned for its distinctive flavor and creamy texture, is a popular choice among cheese enthusiasts, but its fat content often raises questions for those mindful of their dietary intake. Typically, blue cheese contains a relatively high fat content, ranging from 25% to 35% by weight, depending on the variety and production method. This fat contributes to its rich, indulgent mouthfeel and complex taste profile, which includes notes of tanginess and umami. For individuals monitoring their fat consumption, understanding the nutritional composition of blue cheese is essential, as even small portions can significantly impact daily fat intake. Despite its higher fat content, blue cheese is also a good source of protein and calcium, making it a nutrient-dense option when enjoyed in moderation.
Explore related products
What You'll Learn
- Fat Content by Weight: Blue cheese typically contains 25-35% fat by weight
- Serving Size Fat: A 1-ounce serving has about 9-12 grams of fat
- Saturated Fat Levels: Approximately 6-8 grams of saturated fat per ounce
- Caloric Contribution: Fat accounts for 70-75% of blue cheese’s total calories
- Comparison to Other Cheeses: Blue cheese has higher fat content than mozzarella or feta

Fat Content by Weight: Blue cheese typically contains 25-35% fat by weight
Blue cheese, known for its distinct flavor and creamy texture, is a popular choice among cheese enthusiasts. When considering its nutritional profile, one of the most notable aspects is its fat content. Fat Content by Weight: Blue cheese typically contains 25-35% fat by weight, making it a high-fat dairy product. This range is important to understand, as it directly impacts the cheese's caloric density and its role in a balanced diet. For individuals monitoring their fat intake, knowing this percentage allows for better portion control and informed food choices.
The fat content in blue cheese is primarily derived from milk fat, which contributes to its rich and indulgent mouthfeel. The 25-35% fat by weight falls within the typical range for many aged and semi-soft cheeses, though blue cheese often leans toward the higher end due to its production process. During aging, moisture evaporates, concentrating the fat and other components, which is why the fat percentage is expressed as a proportion of the cheese's total weight. This concentration also intensifies the flavor, making blue cheese a favorite for adding depth to dishes despite being used in smaller quantities.
For those tracking macronutrients, understanding that Fat Content by Weight: Blue cheese typically contains 25-35% fat by weight is crucial. A 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of blue cheese, for example, would contain approximately 7 to 10 grams of fat, depending on the exact fat percentage. This makes it a calorie-dense food, with fat contributing the majority of its caloric content. While fat is an essential nutrient, moderation is key, especially for individuals with dietary restrictions or health goals related to fat consumption.
It's worth noting that not all blue cheeses have the same fat content, as variations can occur based on the type of milk used (whole, skim, or a mix) and the specific production methods. Artisanal or specialty blue cheeses may have slightly different fat profiles compared to mass-produced varieties. However, the general range of 25-35% fat by weight remains a reliable guideline for most commercially available blue cheeses. Always checking the nutrition label for precise information is recommended for those with specific dietary needs.
Incorporating blue cheese into a diet while being mindful of its fat content is entirely possible. Its strong flavor means a little goes a long way, allowing for smaller portions that still add significant taste to salads, sandwiches, or cooked dishes. By being aware that Fat Content by Weight: Blue cheese typically contains 25-35% fat by weight, consumers can enjoy this gourmet cheese as part of a balanced and varied diet, savoring its unique qualities without exceeding their fat intake goals.
Mascarpone Cheese Price Guide: Understanding Costs and Budget-Friendly Options
You may want to see also

Serving Size Fat: A 1-ounce serving has about 9-12 grams of fat
When considering the fat content in blue cheese, it's essential to focus on serving size to accurately understand its nutritional impact. A standard serving size for blue cheese is typically 1 ounce, which is a common portion used in dietary guidelines and food labeling. This small yet flavorful amount of blue cheese contains approximately 9 to 12 grams of fat, depending on the specific variety and brand. This range is important to note, as it allows consumers to make informed decisions about their fat intake, especially if they are monitoring their diet for health reasons.
The fat content in a 1-ounce serving of blue cheese is primarily composed of saturated fats, which account for a significant portion of the total fat grams. Saturated fats are a key consideration in dietary planning, as they can impact cholesterol levels and heart health when consumed in excess. Understanding that 9 to 12 grams of fat are present in such a small serving highlights the importance of portion control, especially for individuals aiming to reduce their saturated fat intake. This knowledge empowers consumers to balance their diet while still enjoying blue cheese in moderation.
For those tracking macronutrients or following specific dietary plans, knowing the fat content in a 1-ounce serving of blue cheese is crucial. At 9 to 12 grams of fat, this serving size contributes a notable amount to daily fat allowances, particularly in low-fat diets. It’s also worth noting that blue cheese is calorie-dense, with a significant portion of its calories coming from fat. This makes it a rich addition to meals, but one that should be measured carefully to align with nutritional goals. Pairing blue cheese with lower-fat foods can help create a balanced meal while enjoying its distinctive flavor.
Incorporating blue cheese into a diet while being mindful of its fat content requires strategic planning. A 1-ounce serving, with its 9 to 12 grams of fat, can be a satisfying indulgence when used sparingly. For example, crumbling this amount over a salad or using it as a topping for a lean protein can add depth of flavor without significantly increasing overall fat intake. Being aware of the serving size fat content ensures that blue cheese enhances meals without derailing dietary objectives.
Finally, it’s important to compare the fat content of blue cheese to other cheeses to make informed choices. While blue cheese is higher in fat per ounce compared to some softer cheeses, its strong flavor means a little goes a long way. This can make it a practical option for adding richness to dishes without overconsuming fat. By focusing on the 9 to 12 grams of fat in a 1-ounce serving, individuals can enjoy blue cheese as part of a balanced diet while staying within their nutritional limits. This awareness fosters a healthier relationship with indulgent foods like blue cheese.
Manchego Cheese Price Guide: Cost Factors and Budget Tips
You may want to see also

Saturated Fat Levels: Approximately 6-8 grams of saturated fat per ounce
Blue cheese, known for its distinct flavor and creamy texture, is a popular choice among cheese enthusiasts. However, it’s important to understand its nutritional profile, particularly its saturated fat content. Saturated Fat Levels: Approximately 6-8 grams of saturated fat per ounce is a key aspect to consider when incorporating blue cheese into your diet. This level of saturated fat is relatively high compared to other cheeses, making portion control essential for those monitoring their fat intake.
When examining Saturated Fat Levels: Approximately 6-8 grams of saturated fat per ounce, it’s crucial to place this in the context of daily dietary recommendations. The American Heart Association suggests limiting saturated fat to 5-6% of total daily calories, which equates to about 13 grams for a 2,000-calorie diet. Consuming just one ounce of blue cheese contributes nearly half to two-thirds of this recommended limit. Therefore, enjoying blue cheese in moderation is key to maintaining a balanced diet while still savoring its unique taste.
For individuals with specific health goals, such as managing cholesterol or heart health, understanding Saturated Fat Levels: Approximately 6-8 grams of saturated fat per ounce in blue cheese is particularly important. Saturated fats are known to raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, which can increase the risk of heart disease over time. While blue cheese offers nutritional benefits like protein and calcium, its high saturated fat content necessitates mindful consumption, especially for those with pre-existing health conditions.
Incorporating blue cheese into meals while being aware of Saturated Fat Levels: Approximately 6-8 grams of saturated fat per ounce can be done strategically. Pairing it with fiber-rich foods like whole grains, fruits, or vegetables can help balance the meal and mitigate the impact of saturated fat. Additionally, opting for smaller portions or using blue cheese as a flavor enhancer rather than the main ingredient can allow you to enjoy its richness without exceeding your daily fat intake.
Finally, it’s worth noting that not all blue cheeses have the exact same Saturated Fat Levels: Approximately 6-8 grams of saturated fat per ounce, as variations can exist based on the brand, production method, and milk type (whole, skim, etc.). Checking the nutritional label is always a good practice to ensure accurate information. By staying informed and making conscious choices, you can continue to enjoy blue cheese as part of a healthy and varied diet.
Brie Cheese Fat Content: Uncovering the Creamy Truth and Nutritional Facts
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Caloric Contribution: Fat accounts for 70-75% of blue cheese’s total calories
Blue cheese is renowned for its rich, pungent flavor and creamy texture, but it’s also notable for its high fat content, which significantly contributes to its caloric density. When examining the nutritional profile of blue cheese, it becomes clear that fat is the primary macronutrient driving its calorie count. Specifically, fat accounts for approximately 70-75% of the total calories in blue cheese. This high proportion of fat is a defining characteristic of this cheese variety, setting it apart from lower-fat cheeses like mozzarella or cottage cheese. Understanding this caloric contribution is essential for anyone monitoring their fat intake or overall calorie consumption.
The fat content in blue cheese is primarily composed of saturated fats, which are known for their role in contributing to calorie density. A single ounce (28 grams) of blue cheese typically contains around 6 to 8 grams of fat, with saturated fat making up a significant portion of this total. This high fat content translates to roughly 100-120 calories per ounce, with 70-75% of those calories coming directly from fat. For context, this means that in a 100-calorie serving of blue cheese, approximately 70-75 calories are derived from fat alone. This makes blue cheese a calorie-dense food, where fat is the dominant energy source.
The caloric contribution of fat in blue cheese is particularly important for dietary planning, especially for individuals following low-fat or calorie-restricted diets. While fat is an essential macronutrient that supports various bodily functions, including nutrient absorption and hormone production, consuming high-fat foods like blue cheese in large quantities can quickly add up in terms of calories. For example, a 2-ounce serving of blue cheese could provide around 200 calories, with 140-150 of those calories coming from fat. This highlights the need for portion control when enjoying blue cheese, particularly for those aiming to manage their weight or fat intake.
Despite its high fat content, blue cheese also offers nutritional benefits that should not be overlooked. It is a good source of protein, calcium, and vitamins like vitamin B12. However, the caloric contribution of fat remains the most significant aspect of its nutritional profile. For those who enjoy blue cheese, balancing its consumption with other lower-fat foods can help mitigate its impact on overall calorie and fat intake. Additionally, opting for smaller portions or using blue cheese as a flavor enhancer rather than a main ingredient can allow individuals to savor its unique taste without overconsuming fat.
In summary, the statement "fat accounts for 70-75% of blue cheese's total calories" underscores the cheese's high caloric density and its reliance on fat as the primary energy source. This makes blue cheese a food that should be consumed mindfully, especially for those monitoring their fat or calorie intake. By understanding this caloric contribution, individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating blue cheese into their diet while maintaining a balanced and healthy approach to nutrition.
Unveiling the Salary of Chuck E. Cheese's Iconic Mascot
You may want to see also

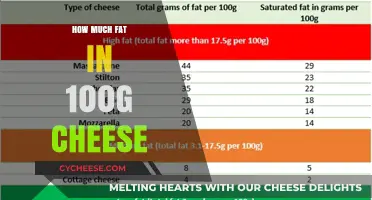
Comparison to Other Cheeses: Blue cheese has higher fat content than mozzarella or feta
When comparing the fat content of blue cheese to other popular varieties, it becomes evident that blue cheese stands out for its higher fat concentration. Blue cheese typically contains around 30-35 grams of fat per 100 grams, which is significantly higher than many other cheeses. This is largely due to its rich, creamy texture and the specific aging process it undergoes, which contributes to its distinctive flavor and fat profile. In contrast, cheeses like mozzarella and feta are known for their lower fat content, making them popular choices for those seeking lighter options.
Mozzarella, a staple in Italian cuisine, is renowned for its low fat content, usually ranging from 17 to 22 grams of fat per 100 grams. This makes it a preferred choice for dishes like pizza and caprese salads, where a lighter cheese is desired. The lower fat content in mozzarella is partly due to its production process, which involves stretching and kneading the curd, resulting in a cheese that retains less fat. When compared to blue cheese, mozzarella’s fat content is nearly half, highlighting the stark difference between these two cheeses.
Feta, a brined cheese commonly used in Mediterranean dishes, also has a lower fat content compared to blue cheese. Feta typically contains around 20-25 grams of fat per 100 grams, depending on the milk used (sheep, goat, or cow). Its crumbly texture and tangy flavor make it a versatile ingredient, but its fat content remains modest. Like mozzarella, feta’s fat levels are significantly lower than those of blue cheese, making it a healthier alternative for fat-conscious consumers.
The higher fat content in blue cheese can be attributed to its production method, which involves the introduction of Penicillium cultures to create the characteristic veins and rich flavor. This process often requires higher-fat milk, such as from cows, to achieve the desired texture and taste. In contrast, mozzarella and feta are often made from lower-fat milk or undergo processes that reduce fat retention, resulting in their lighter profiles. This comparison underscores why blue cheese is considered more indulgent and why it may not be the best choice for those strictly monitoring their fat intake.
For individuals comparing cheeses based on fat content, the choice between blue cheese, mozzarella, and feta depends on dietary preferences and goals. While blue cheese offers a rich, bold flavor due to its higher fat content, mozzarella and feta provide lighter alternatives without sacrificing taste. Understanding these differences allows consumers to make informed decisions, whether they’re crafting a gourmet cheese board or preparing a health-conscious meal. In summary, blue cheese’s fat content clearly surpasses that of mozzarella and feta, making it a standout—though more indulgent—option in the world of cheeses.
Mini Babybel Cheese Price Guide: Costs and Budget-Friendly Tips
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of blue cheese contains approximately 7–10 grams of fat, depending on the variety and brand.
Yes, blue cheese is relatively high in saturated fat, with about 5–7 grams of saturated fat per 1-ounce serving.
Blue cheese is moderately high in fat compared to other cheeses. For example, mozzarella has about 4–6 grams of fat per ounce, while cream cheese has around 5–9 grams per ounce.