Dairy products are known to have anti-inflammatory effects, and cheese is no exception. However, when it comes to cheddar cheese, the answer is a bit more complex. While cheese itself doesn't directly cause inflammation, certain types of cheddar cheese, especially those with high saturated fat content, may contribute to inflammation. This is because a diet high in saturated fats is known to increase inflammation in the body. On the other hand, cheese is a good source of calcium and protein, and when paired with the right foods, it can be part of a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet.
Is Cheddar Cheese Anti-Inflammatory?
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Cheddar Cheese Anti-Inflammatory | No |
| Reason | High saturated fat content |
| Recommended Consumption | 3.5-5 grams of saturated fat per ounce |
| Pairing | Fibre-rich food and healthy fats |
| Alternatives | Low-fat cheese, Swiss cheese |
Explore related products
$21.99
$7.83 $17.99
What You'll Learn
- Cheddar cheese and inflammation: the role of saturated fat
- Cheddar cheese and inflammation: the importance of food pairings
- Cheddar cheese and inflammation: the impact of lactose intolerance
- Cheddar cheese and inflammation: the benefits of probiotics
- Cheddar cheese and inflammation: the role of calcium and other nutrients

Cheddar cheese and inflammation: the role of saturated fat
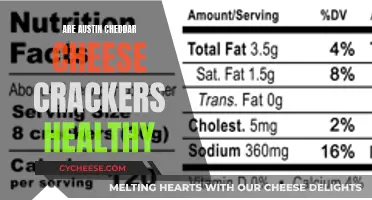
While cheese in itself does not cause inflammation, the saturated fat content of some cheeses may be of concern. Cheddar cheese is one such example, with a 1-ounce serving of whole-milk Cheddar cheese containing 5 grams of saturated fat and 120 calories. The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting saturated fat to no more than 10% of one's daily caloric intake.
The role of saturated fat in inflammation is well-established. A diet high in saturated fats can increase inflammation in the body. Cheddar cheese, being a full-fat dairy product, is rich in saturated fats, which have been linked to higher levels of inflammation. This is particularly true when compared to other dairy products like milk or yogurt, which have lower saturated fat content. For example, a 6-ounce container of whole-milk plain yogurt contains only 3.5 grams of saturated fat.
However, it is important to note that the link between dairy and inflammation is complex and the results of studies are not always consistent. While some studies have found that dairy products can increase inflammation, others have concluded that dairy has anti-inflammatory effects. For example, a 2017 review of 52 clinical studies published in Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition found that dairy generally has anti-inflammatory properties, except in individuals allergic to cow's milk.
Furthermore, the type of dairy product and its other nutrients may play a role in inflammation. For instance, fermented dairy products or those with added probiotics, such as yogurt, buttermilk, kefir, and cottage cheese, are thought to have anti-inflammatory benefits. The probiotics in Swiss cheese have also been found to decrease inflammation. Additionally, the way cheese is paired with other foods and the quantity consumed may contribute to its inflammatory potential.
Overall, while cheddar cheese contains saturated fat, which is associated with inflammation, the relationship between dairy and inflammation is multifaceted. The effects of cheddar cheese on inflammation may depend on various factors, including the quantity consumed, the foods it is paired with, and individual differences in lactose tolerance and allergies.
Dubliner Cheddar Cheese: A Tasty Irish Treat
You may want to see also

Cheddar cheese and inflammation: the importance of food pairings
While cheese in itself does not cause inflammation, the saturated fat content of some cheeses may be of concern as this type of fat is associated with inflammation. Cheddar cheese is one such cheese that contains saturated fat. For example, a 1-ounce serving of whole-milk Cheddar cheese contains 5 grams of saturated fat. The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting saturated fat to no more than 10% of one's daily caloric intake.
However, dairy foods, including cheese, are a great way to get calcium and protein in the diet. Dairy foods can be problematic for some, but they can also be anti-inflammatory for others. Fermented dairy or dairy with added probiotics can be beneficial for overall health. Dairy products that may help reduce inflammation include yogurt, buttermilk, kefir, cottage cheese, and aged cheese.
Therefore, when including cheddar cheese in your diet, it is important to consider the food pairings to ensure that the meal as a whole is not inflammatory. As a general rule of thumb, you can use the following formula when balancing your plate with cheese: Cheese + fiber-rich food + healthy fat. For example, you can pair low-fat Cheddar cheese with black beans, salsa, and guacamole in a quesadilla. Another idea is to add a tablespoon or two of farmer’s cheese to an omelet with spinach and serve it with some fresh fruit.
In addition to food pairings, it is also important to consider the quantity of cheddar cheese consumed. Cheese is often used in large quantities in dishes such as pizza, tacos, grilled cheese, and macaroni and cheese, which can contribute to inflammation. Therefore, it is recommended to consume cheese in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Finding Grated Sharp Cheddar Cheese: Best Sources and Options
You may want to see also

Cheddar cheese and inflammation: the impact of lactose intolerance
While cheese in itself does not cause inflammation, it is often paired with other foods that contain saturated fat, such as ground beef in lasagna or pepperoni on pizza. This can make cheese-containing meals more inflammatory than other forms of dairy. For example, a 1-ounce serving of whole-milk Cheddar cheese contains 5 grams of saturated fat, whereas a 6-ounce container of whole-milk plain yogurt contains 3.5 grams.
The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting saturated fat to no more than 10% of one's daily caloric intake. The American Heart Association is more conservative, recommending that foods with saturated fat should account for just 5 to 6 percent of daily calories.
Lactose intolerance can cause symptoms such as gas, diarrhea, and bloating after consuming milk or other dairy products. However, it is important to note that lactose intolerance is different from a milk allergy, which is an immune response to the proteins in milk. While lactose intolerance can cause digestive issues, it is not directly linked to inflammation.
People who are lactose intolerant may still be able to tolerate cheese, especially aged cheeses like Cheddar, as they contain little to no lactose. During the cheese-making process, milk is cultured with lactic acid bacteria, which breaks down the lactose. Aged cheeses are further matured, allowing more time for lactose to be broken down. As a result, aged cheeses are generally well-tolerated by those with lactose intolerance.
In addition, some studies have found that fermented dairy products, such as yogurt and kefir, may have anti-inflammatory properties due to their probiotic content. These good bacteria support gut health and immune function, which can help regulate inflammation in the body.
Overall, while Cheddar cheese may not directly cause inflammation, it is important to consider the overall dietary pattern and the quantity and frequency of cheese consumption, especially for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Pairing cheese with anti-inflammatory foods, such as fiber-rich and antioxidant-rich options, can help balance the meal and potentially reduce any inflammatory effects.
Mature Cheddar Cheese Syns: Everything You Need to Know
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Cheddar cheese and inflammation: the benefits of probiotics
While cheese is often included in the traditional Western diet, it is important to remember that it is high in saturated fat, which is associated with inflammation. However, this does not mean that cheese lovers need to cut out cheddar cheese entirely. Instead, it is recommended to be mindful of the quantity and pairings when consuming cheddar cheese to maintain an anti-inflammatory diet.
Cheddar cheese, like other dairy products, can be a good source of calcium and protein. It is also worth noting that dairy products with added or natural probiotics can have anti-inflammatory benefits. These probiotics introduce ""good"" bacteria to the gut, supporting immune function and nutrient absorption.
When incorporating cheddar cheese into your diet, consider pairing it with foods that are rich in antioxidants and fibre. For example, a quesadilla with low-fat cheddar cheese, black beans, salsa, and guacamole can be a delicious and nutritious option. Including such pairings in your meals can help balance the plate and increase your intake of other nutritious foods.
Additionally, opting for reduced-fat cheddar cheese can be a simple way to reduce saturated fat intake. According to the 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, it is recommended to limit saturated fat to no more than 10% of daily caloric intake. By being mindful of these suggestions, you can still enjoy the benefits of cheddar cheese while maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
In conclusion, while cheddar cheese can be a part of a balanced diet, it is important to be mindful of its saturated fat content and its pairings to maintain an anti-inflammatory diet. Including probiotics, antioxidants, and fibre-rich foods along with your cheddar cheese can provide additional health benefits and support overall well-being.
Cheddar Cheese: A Lactose Intolerant's Friend or Foe?
You may want to see also

Cheddar cheese and inflammation: the role of calcium and other nutrients
While cheese in itself does not cause inflammation, the saturated fat content of some cheeses may be of concern as this type of fat is associated with inflammation. Cheddar cheese is one such example, with a 1-ounce serving of whole-milk Cheddar cheese containing 120 calories and 5 grams of saturated fat. The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting saturated fat to no more than 10% of one's daily caloric intake.
However, dairy foods, including cheese, are a great way to get calcium and protein in the diet. Calcium has been listed as a nutrient of public health concern. Dairy products that may help reduce inflammation include yogurt, buttermilk, kefir, cottage cheese, and aged cheese. Yogurt is packed with nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, vitamin B12, zinc, phosphorus, and magnesium, depending on the type. Similarly, kefir contains many essential nutrients, including vitamin D, vitamin A, and bioactive compounds such as lactic and acetic acids.
Cheese can be included in an anti-inflammatory diet by pairing it with other foods rich in antioxidants to help balance your meals and increase the intake of other nutritious foods. For example, cottage cheese pairs great with antioxidant-rich berries and heart-healthy walnuts. Another option is to consider switching to Swiss cheese, as one study found that the probiotics in this variety could decrease inflammation.
Cheddar Cheese: A Natural Probiotic?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The saturated fat in many cheeses, including cheddar, can contribute to inflammation. However, cheese also contains other fatty acids that have been linked to health benefits such as a reduced risk of diabetes.
A 1-ounce serving of whole-milk Cheddar cheese contains 5 grams of saturated fat and 185 milligrams of sodium.
The American Heart Association recommends that foods with saturated fat should account for just 5 to 6 percent of your daily calories. The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting saturated fat to no more than 10% of one’s daily caloric intake.
Pair low-fat cheese with other foods rich in antioxidants to help balance your meals and increase your intake of other nutritious foods. For example, you could make a quesadilla with low-fat Cheddar cheese, black beans, salsa, and guacamole.