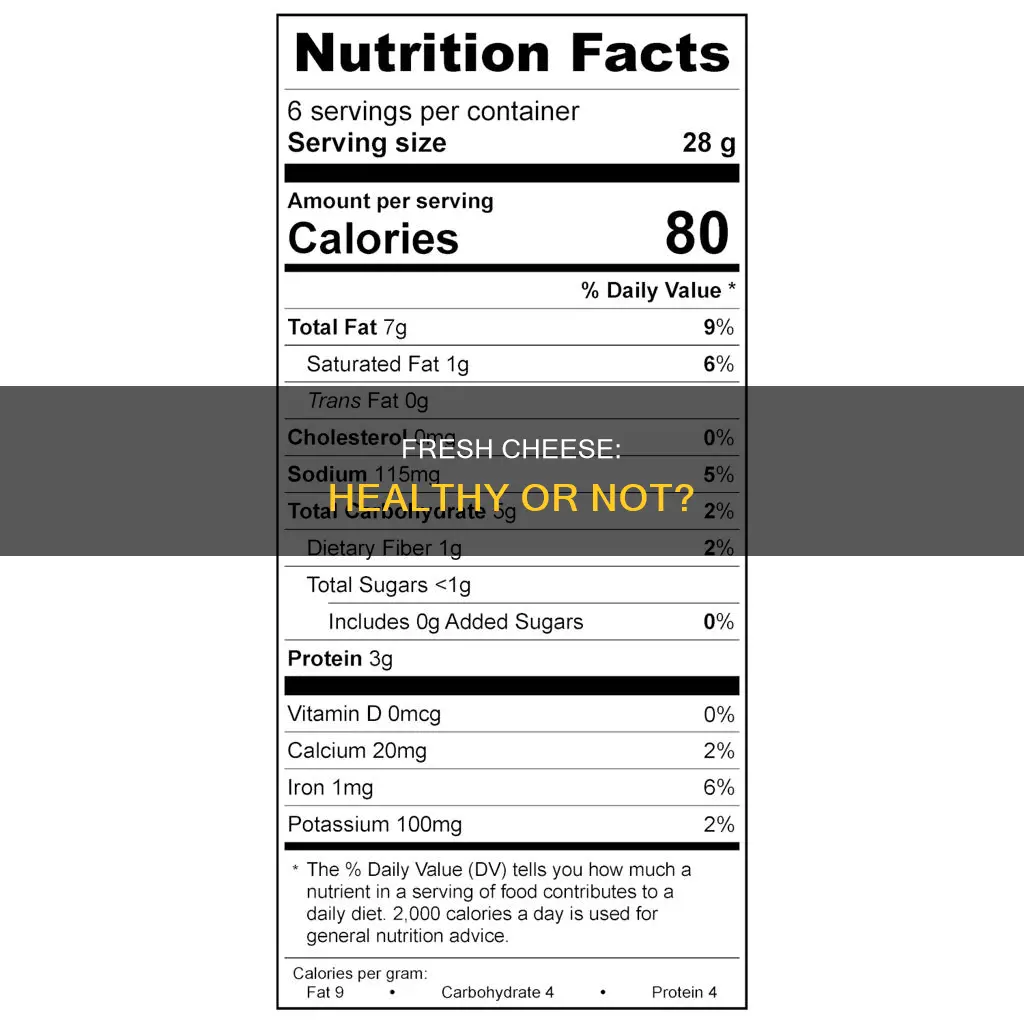
Cheese is a staple in many diets and is a great source of calcium and protein. Fresh cheeses like ricotta and cottage cheese are generally high in moisture and soft in texture. They are ready to be eaten quickly without needing time to age. While cheese is a healthy and delicious source of many nutrients, it can also be high in saturated fats and sodium. The health benefits of cheese depend on the individual and the type and amount of cheese consumed.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Nutritional benefits | Cheese is a good source of calcium, protein, vitamins A, D, and B, potassium, and iodine. |
| Health benefits | Cheese may have a positive effect on cardiovascular health, dental health, and bone health. |
| Health risks | Cheese can be high in sodium, saturated fat, and cholesterol, which can increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. Soft and blue-veined cheeses may be contaminated with listeria if made with unpasteurized milk. |
| Types of fresh cheese | Fresh cheeses include ricotta, cottage cheese, mozzarella, Brie, goat cheese, and halloumi. |
| Healthiest types of fresh cheese | Mozzarella is lower in sodium and calories than most other cheeses and contains probiotics that may improve gut health and immunity. Ricotta is also lower in calories and fat. |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn

Fresh cheese is a good source of calcium and protein
Fresh cheeses, such as ricotta, cottage cheese, and mozzarella, are generally high in moisture and soft in texture. They are ready to be eaten quickly, without needing time to age.
Mozzarella, for example, is lower in sodium and calories than most other cheeses. It also contains bacteria that act as probiotics, which may improve gut health and promote immunity. Cottage cheese is also high in protein and low in calories, making it a good option for weight loss.
However, it is important to note that cheese can also be high in saturated fats and sodium, which can have negative health impacts when consumed in excess. Therefore, fresh cheese should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
In addition to calcium and protein, cheese is also a source of other nutrients such as vitamins A, D, and B, as well as potassium and iodine.
Recognizing a Healthy Swiss Cheese Plant
You may want to see also

It can be high in sodium and saturated fats
Cheese is a whole food, and whole foods are generally considered good for health. It is a good source of calcium, protein, vitamins, and probiotics. However, cheese can also be high in sodium and saturated fats, which can have adverse health effects.
Sodium is a necessary nutrient for the human body, but its excessive intake can increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. Fresh cheeses like feta are often packaged in brine to preserve freshness, and they can be high in sodium. Aged cheeses like cheddar, Parmesan, and Swiss are also stored and sold after maturing, leading to a stronger flavour and higher salt content. Processed cheese products, such as American cheese, are made by mixing cheese with other dairy products and adding ingredients to enhance flavour and storage time. These processed cheeses tend to be higher in sodium than other varieties.
High intake of saturated fats can increase the risk of diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular problems. Full-fat cheeses are known to be high in saturated fats. If you are concerned about the cholesterol and saturated fat content of full-fat cheeses, consider using them sparingly as a condiment. Grass-fed cheese may be a healthier option as it provides a better balance of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for heart and metabolic health.
While cheese can be a part of a healthy diet, moderation is key. The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting saturated fat intake to less than 10% of daily total calories. This means that for an 1800-calorie diet, saturated fat intake should be below 20 grams per day. Additionally, some cheeses may be contaminated with listeria, especially if made with unpasteurized milk. Soft, fresh cheeses like mozzarella may trigger lactose intolerance in some individuals.
American Cheese: Healthy or Unhealthy?
You may want to see also

Fresh cheese is usually high in moisture and soft in texture
Fresh cheese, such as ricotta, cottage cheese, and mozzarella, is usually high in moisture and soft in texture. These cheeses are ready to be eaten quickly and do not need time to age. Fresh, soft cheeses are often higher in lactose and can trigger a reaction in lactose-intolerant people. They can also sometimes become contaminated with listeria, especially if they are made with unpasteurized or "raw" milk.
Mozzarella, for example, is lower in sodium and calories than most other cheeses. It also contains bacteria that act as probiotics, which may improve gut health, promote immunity, and decrease inflammation.
Ricotta is also a healthy option, as it is much lower in calories and fat than other cheeses. Cottage cheese is another fresh cheese that is high in protein and low in calories, making it a good option for weight loss.
Overall, fresh, soft cheeses can be part of a healthy diet, but they should be consumed in moderation, especially for those with lactose intolerance or other dietary restrictions. It's important to consider the individual's overall diet and health needs when determining the appropriate amount of fresh cheese to include.
Cheese and Pepperoni: Healthy Snack or Unhealthy Treat?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

It's a whole food, so it's generally healthy in moderation
Cheese is considered a whole food, and whole foods are generally healthy. However, it's important to consume whole foods in moderation, as part of a balanced diet. Cheese is a good source of calcium, fat, and protein, and it also contains vitamins A, D, and B, as well as potassium and iodine.
Fresh cheeses, such as ricotta and cottage cheese, are generally high in moisture and soft in texture. They are ready to be consumed without needing time to age. Cottage cheese, in particular, is often recommended for weight loss due to its high protein and low-calorie content. A 2019 study found that consuming 3g of CLA (conjugated linoleic acid) supplements, found in feta cheese, per day for 3 months was associated with decreased body fat mass.
Mozzarella is another healthy option, as it is lower in sodium and calories compared to other cheeses. It also contains bacteria that act as probiotics, which may improve gut health, promote immunity, and decrease inflammation. Blue cheese is also high in calcium, which is necessary for optimal bone health.
However, it's important to be mindful of the potential downsides of consuming cheese. Cheese can be high in sodium, which can negatively impact bone health by increasing calcium loss through urine. Soft and blue-veined cheeses may become contaminated with listeria, especially if made with unpasteurized or "raw" milk. Additionally, some individuals may have allergies or intolerances to dairy products, making cheese unsuitable for them.
In conclusion, fresh cheese can be considered generally healthy when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. However, it is important to be mindful of potential health concerns and adjust intake accordingly.
Block Cheese vs Shredded: Which is Healthier?
You may want to see also

Fresh cheese may be contaminated with listeria if made with raw milk
Fresh cheese is generally considered healthy. It is a good source of calcium, fat, and protein. However, it is important to note that fresh cheese, particularly soft cheese, may be contaminated with Listeria monocytogenes if made with raw or unpasteurized milk. Listeria infection can be severe for certain high-risk groups, including pregnant women, newborns, adults over 65, and immunocompromised individuals.
Listeria monocytogenes is a type of bacteria that can cause listeriosis, a foodborne illness. It has been the most common cause of cheese-related recalls in the United States and Canada in recent years. While good farming practices can reduce the risk of contamination, they cannot guarantee the absence of harmful bacteria. Pasteurized milk offers the same nutritional benefits as raw milk without the associated risks.
Soft cheeses, such as queso fresco, ricotta salata, and cotija, have been implicated in listeriosis outbreaks. Listeria can survive refrigeration temperatures and easily spread to other foods and surfaces. Cross-contamination can occur during the cutting and recutting of cheese wheels at various stages of the supply chain, increasing the number of affected units and the geographical reach of contaminated products.
To minimize the risk of listeria contamination, the CDC recommends opting for pasteurized milk and dairy products. Consumers who purchase recalled products should thoroughly clean and sanitize any surfaces or containers that came into contact with the cheese. Additionally, following the FDA's safe handling and cleaning guidelines can help reduce the likelihood of cross-contamination.
In conclusion, while fresh cheese is generally considered a healthy food choice, it is important to be aware of the potential risk of Listeria contamination when consuming soft cheeses made with raw milk. Opting for pasteurized dairy products and practicing proper food handling and sanitation can help mitigate this risk.
Subway Steak and Cheese: Healthy or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Fresh cheeses are generally high in moisture and soft in texture. They are ready to be eaten quickly without needing time to age. Fresh cheeses can be healthy as they are a good source of calcium and protein. However, they can also be high in saturated fats and sodium. Therefore, it is recommended to consume fresh cheese in moderation as part of a healthy dietary eating plan.
Some examples of fresh cheese include mozzarella, ricotta, cottage cheese, and feta.
Fresh cheese can be high in sodium, which can increase calcium loss through urine, potentially impacting bone health. Soft, fresh cheeses can sometimes become contaminated with listeria, especially if they are made with unpasteurized or raw milk. Additionally, fresh cheeses are often higher in lactose and may trigger a reaction in lactose-intolerant individuals.











































