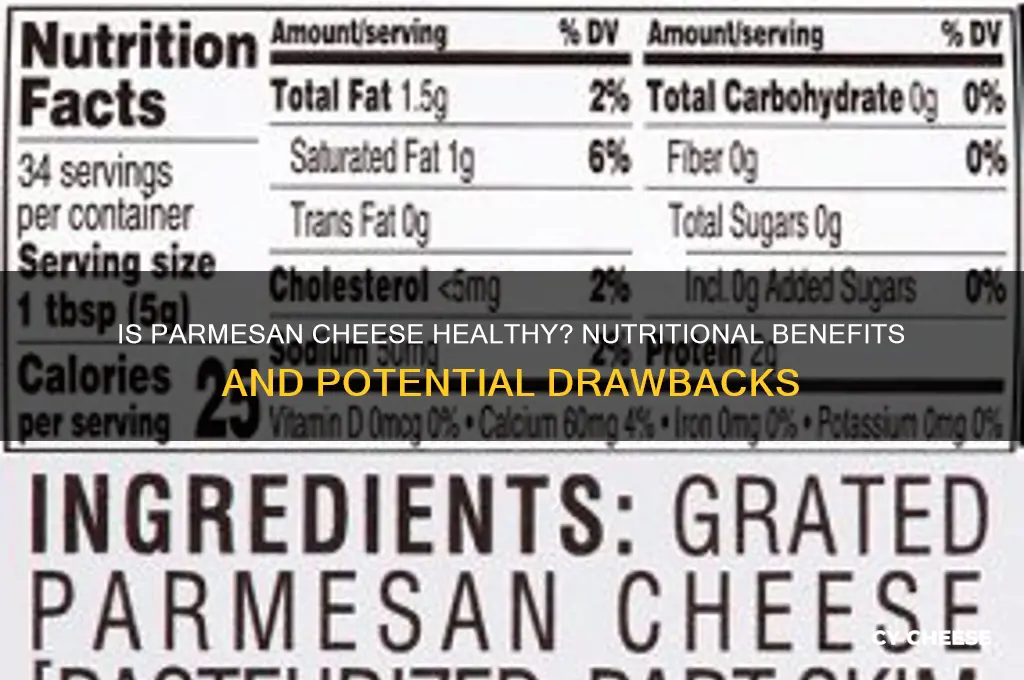
Parmesan cheese, a staple in many kitchens, is often celebrated for its rich flavor and versatility, but its health benefits are a topic of interest and debate. While it is a good source of protein, calcium, and essential nutrients like vitamin B12 and phosphorus, it is also high in saturated fat and sodium, which can be concerning for those monitoring their heart health or blood pressure. Moderation is key, as incorporating small amounts of Parmesan into a balanced diet can provide nutritional advantages without the drawbacks. Additionally, its probiotic properties, thanks to the fermentation process, may support gut health. Ultimately, whether Parmesan cheese is good for you depends on individual dietary needs and overall consumption habits.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Nutrient Density | High in protein, calcium, phosphorus, vitamin B12, zinc, and selenium. |
| Caloric Content | Approximately 130 calories per ounce (28 grams). |
| Protein Content | About 10 grams of protein per ounce, supporting muscle health and satiety. |
| Calcium Content | Provides around 330 mg of calcium per ounce, promoting bone and dental health. |
| Fat Content | Contains about 8 grams of fat per ounce, mostly saturated fat. |
| Cholesterol | Approximately 15 mg of cholesterol per ounce. |
| Sodium Content | High sodium levels, around 170 mg per ounce, which may be a concern for those monitoring salt intake. |
| Lactose Content | Very low lactose due to the aging process, making it easier to digest for lactose-intolerant individuals. |
| Probiotics | May contain beneficial bacteria due to fermentation, though levels are lower compared to softer cheeses. |
| Aging Process | Aged for at least 12 months, enhancing flavor and reducing lactose content. |
| Portion Control | Often used in small amounts as a flavor enhancer, which can help manage calorie intake. |
| Potential Health Benefits | Supports bone health, muscle repair, and immune function due to its nutrient profile. |
| Potential Drawbacks | High sodium and saturated fat content may pose risks for heart health if consumed in excess. |
| Dietary Considerations | Suitable for low-lactose diets but not for vegan or dairy-free diets. |
| Moderation Recommendation | Best consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn
- Nutritional Benefits: High in protein, calcium, and vitamins, supporting bone health and muscle function
- Low in Calories: A small serving adds flavor without significantly increasing calorie intake
- Lactose Content: Contains minimal lactose, making it easier to digest for some individuals
- Sodium Concerns: High sodium levels may pose risks for those with hypertension or heart issues
- Portion Control: Overconsumption can lead to excessive calorie and fat intake, requiring moderation

Nutritional Benefits: High in protein, calcium, and vitamins, supporting bone health and muscle function
Parmesan cheese is renowned for its rich flavor and versatility in cooking, but it also offers significant nutritional benefits, particularly in supporting bone health and muscle function. One of its standout qualities is its high protein content. Protein is essential for repairing tissues, building muscle, and maintaining overall body function. A single ounce of Parmesan cheese provides about 10 grams of protein, making it an excellent choice for those looking to increase their protein intake, especially in diets that may be lacking in this macronutrient. This high protein content also contributes to satiety, helping to curb hunger and support weight management.
In addition to protein, Parmesan cheese is an exceptional source of calcium, a mineral critical for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Calcium plays a vital role in bone density and structure, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures as we age. Just one ounce of Parmesan delivers approximately 330 milligrams of calcium, which is about 30% of the daily recommended intake for adults. Incorporating Parmesan into your diet can be an effective way to boost calcium levels, particularly for individuals who may not consume enough dairy products or other calcium-rich foods.
Beyond protein and calcium, Parmesan cheese is packed with essential vitamins that further enhance its nutritional profile. It is particularly rich in vitamin B12, which is crucial for nerve function, DNA synthesis, and the formation of red blood cells. Parmesan also contains notable amounts of vitamin A, which supports immune function, skin health, and vision. Additionally, it provides vitamin K2, a lesser-known but important nutrient that works synergistically with calcium to improve bone health and cardiovascular wellness by ensuring calcium is deposited in bones and teeth rather than arteries.
The combination of protein, calcium, and vitamins in Parmesan cheese makes it a powerful ally for muscle function and overall health. Protein is fundamental for muscle repair and growth, while calcium and vitamin D (often added to fortified cheeses) work together to optimize muscle contractions and nerve signaling. Vitamin B12 and other B vitamins in Parmesan also play a role in energy production, ensuring muscles have the fuel they need during physical activity. For athletes or individuals engaged in regular exercise, incorporating Parmesan into meals can be a delicious way to support muscle recovery and performance.
Lastly, the nutritional benefits of Parmesan cheese extend to its role in a balanced diet. Its high nutrient density means you can obtain significant amounts of protein, calcium, and vitamins in relatively small portions, making it an efficient addition to meals. Whether grated over salads, sprinkled on soups, or enjoyed in moderation as a snack, Parmesan can enhance both the flavor and nutritional value of your diet. However, it’s important to consume it mindfully, as it is also high in calories and sodium, which should be considered for those monitoring their intake of these components. Overall, when enjoyed as part of a balanced diet, Parmesan cheese can be a nutritious and beneficial addition to support bone health, muscle function, and overall well-being.
Colby Jack Cheese: The Perfect Sandwich Addition?
You may want to see also

Low in Calories: A small serving adds flavor without significantly increasing calorie intake
Parmesan cheese is a popular choice for those looking to add a burst of flavor to their dishes without the guilt of excessive calorie consumption. One of its most appealing qualities is its low-calorie content, making it an excellent option for health-conscious individuals. A small serving of Parmesan, typically around 1 tablespoon (about 5-7 grams), contains approximately 20-22 calories. This minimal calorie contribution allows you to enhance the taste of your meals without derailing your dietary goals. For instance, sprinkling a bit of Parmesan over a salad or pasta dish can elevate its flavor profile while keeping the overall calorie count in check.
The low-calorie nature of Parmesan cheese is particularly beneficial for those following calorie-restricted diets or aiming to manage their weight. Unlike other cheeses that can be calorie-dense, Parmesan provides a concentrated flavor punch without the added calories. This makes it a smart substitute for higher-calorie cheese options in recipes. For example, using grated Parmesan as a topping instead of shredded cheddar or mozzarella can significantly reduce the calorie content of a dish while maintaining its savory appeal. Its intense flavor means a little goes a long way, ensuring you don’t need to use large quantities to achieve the desired taste.
Incorporating Parmesan cheese into your meals is also a practical way to satisfy cravings for cheesy flavors without overindulging. Its low-calorie profile aligns with mindful eating practices, allowing you to enjoy your favorite dishes without feeling deprived. Additionally, Parmesan’s umami-rich taste can make lighter, lower-calorie meals more satisfying. For instance, a sprinkle of Parmesan on roasted vegetables or a bowl of soup can transform a simple dish into a more indulgent experience without adding substantial calories. This makes it an ideal ingredient for those striving to balance flavor and nutrition.
Another advantage of Parmesan’s low-calorie content is its versatility in various dietary plans, including low-carb, keto, and Mediterranean diets. Its minimal impact on calorie intake makes it a valuable addition to these eating styles, where flavor enhancement is often key to adherence. Furthermore, Parmesan’s nutritional density—packed with protein, calcium, and other essential nutrients—ensures that you’re not just getting flavor but also health benefits without the calorie burden. This combination of low calories and high nutritional value makes Parmesan a standout choice for anyone looking to eat healthily without sacrificing taste.
In summary, Parmesan cheese’s low-calorie attribute is a significant advantage for those seeking to add flavor to their meals without compromising their dietary objectives. A small serving delivers a robust taste while contributing negligibly to calorie intake, making it a perfect ingredient for weight management and health-focused eating. Whether used as a topping, seasoning, or ingredient, Parmesan allows you to enjoy the richness of cheese without the calorie concerns associated with other varieties. Its ability to enhance dishes with minimal calories underscores its role as a smart and flavorful addition to any balanced diet.
Freezing Cheese: How Long Does It Stay Fresh and Safe to Eat?
You may want to see also

Lactose Content: Contains minimal lactose, making it easier to digest for some individuals
Parmesan cheese is renowned for its rich flavor and versatility in cooking, but one of its most notable health attributes is its minimal lactose content. Lactose, a sugar found in milk, can be difficult for some individuals to digest due to lactose intolerance. When cheese is produced, much of the lactose is removed during the curdling and aging process. Parmesan, in particular, undergoes an extensive aging period—typically 12 to 36 months—which significantly reduces its lactose content. This makes it a more digestible option for those who are lactose intolerant compared to fresher, softer cheeses.
The minimal lactose content in Parmesan cheese is a result of the fermentation process that occurs during aging. As the cheese matures, bacteria break down the lactose into lactic acid, which not only reduces lactose levels but also contributes to the cheese's distinctive tangy flavor. For individuals with lactose intolerance, this means that consuming Parmesan is less likely to cause digestive discomfort such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea. However, it’s important to note that while Parmesan contains very little lactose, it is not entirely lactose-free, so highly sensitive individuals should still consume it in moderation.
For those who are lactose intolerant, Parmesan cheese can be a valuable addition to their diet, providing a way to enjoy the flavor and nutritional benefits of cheese without the adverse effects of lactose. It is also a good source of protein, calcium, and essential nutrients like vitamin B12 and phosphorus, making it a nutritious choice. The low lactose content ensures that these benefits can be accessed by a broader range of people, including those with mild to moderate lactose intolerance.
When incorporating Parmesan into a diet, it’s beneficial to consider portion sizes, as even small amounts can add significant flavor to dishes. Grating Parmesan over salads, soups, or pasta allows you to use less while still enhancing the taste. This approach maximizes its digestibility and nutritional value without overloading on calories or fat. Additionally, opting for high-quality, traditionally aged Parmesan ensures the lowest possible lactose content, as mass-produced varieties may not undergo the same lengthy aging process.
In summary, the minimal lactose content in Parmesan cheese makes it an excellent option for individuals seeking to enjoy cheese without the digestive issues associated with lactose. Its extended aging process naturally reduces lactose levels, allowing those with lactose intolerance to savor its flavor and reap its nutritional benefits. By choosing Parmesan thoughtfully and in appropriate portions, it can be a healthy and delicious addition to a balanced diet.
Deli Mozzarella Cheese Shelf Life: How Long Does It Last?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Sodium Concerns: High sodium levels may pose risks for those with hypertension or heart issues
Parmesan cheese, while celebrated for its rich flavor and nutritional benefits, raises concerns due to its high sodium content. A single ounce of Parmesan can contain upwards of 400 milligrams of sodium, which is a significant portion of the recommended daily intake of 2,300 milligrams or less, as advised by health organizations. For individuals with hypertension or heart issues, this high sodium level can exacerbate health problems. Sodium is known to increase blood pressure by causing the body to retain water, putting additional strain on the heart and blood vessels. Therefore, those with cardiovascular concerns must monitor their sodium intake carefully, and the sodium content in Parmesan cheese should be a consideration in their dietary choices.
For people with hypertension, the risks associated with high sodium intake are particularly pronounced. Consuming foods like Parmesan cheese in excess can lead to elevated blood pressure levels, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular complications. The American Heart Association emphasizes that reducing sodium intake is crucial for managing blood pressure, and even small reductions can have a positive impact on heart health. While Parmesan can be a flavorful addition to meals, individuals with hypertension should consider using it sparingly or exploring lower-sodium alternatives to mitigate these risks.
Heart health is another critical area where high sodium intake, including from Parmesan cheese, can pose risks. Excess sodium contributes to arterial stiffness and can worsen conditions like congestive heart failure, where the heart struggles to pump blood efficiently. For those with existing heart issues, the added sodium from Parmesan could lead to fluid retention, making it harder for the heart to function properly. It is essential for individuals with heart conditions to consult with healthcare providers or dietitians to determine safe portion sizes or alternatives that align with their dietary needs.
Despite its sodium concerns, Parmesan cheese can still be enjoyed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. For those without hypertension or heart issues, the occasional use of Parmesan may not pose significant risks. However, for individuals with these health concerns, mindful consumption is key. Opting for reduced-sodium versions of Parmesan or using smaller quantities can help balance flavor preferences with health needs. Additionally, pairing Parmesan with potassium-rich foods, such as vegetables, can help counteract some of the negative effects of sodium on blood pressure.
In summary, while Parmesan cheese offers nutritional benefits like protein and calcium, its high sodium content makes it a food of caution for those with hypertension or heart issues. Understanding the risks associated with sodium intake and adopting strategies to limit consumption can help individuals enjoy Parmesan without compromising their health. Always consult with a healthcare professional to tailor dietary choices to specific health conditions and ensure that sodium intake remains within safe limits.
Cheese and Crackers: The Perfect Late-Night Snack?
You may want to see also

Portion Control: Overconsumption can lead to excessive calorie and fat intake, requiring moderation
Parmesan cheese, while packed with nutrients like protein, calcium, and vitamins, can become a dietary concern when consumed in excess. Portion control is crucial because Parmesan is calorie-dense, with about 120 calories per ounce (28 grams). Its high fat content, primarily saturated fat, contributes significantly to its caloric load. Overconsumption can easily lead to an unintended increase in daily calorie intake, which, over time, may contribute to weight gain or other health issues. Moderation is key to enjoying its benefits without the drawbacks.
One of the challenges with Parmesan is its strong flavor, which often encourages overuse. A little goes a long way, but it’s easy to sprinkle more than a single serving on pasta, salads, or soups. Measuring portions is an effective strategy to avoid overconsumption. A typical serving size is about 1 tablespoon (5-7 grams), which contains roughly 20-25 calories. Using measuring spoons or a kitchen scale can help ensure you stay within a healthy range, especially if you’re monitoring your calorie or fat intake.
Another aspect of portion control is mindful eating. Parmesan’s savory, umami flavor can make it tempting to add more than necessary. Being aware of how much you’re using and savoring each bite can reduce the urge to overindulge. For example, instead of mindlessly sprinkling cheese over a dish, grate a measured amount and distribute it evenly. This not only helps control portions but also ensures you’re getting the flavor without excess calories.
Incorporating Parmesan into a balanced diet requires planning and awareness. If you’re using it as a topping, consider reducing other high-calorie ingredients in the meal to compensate. For instance, if you add Parmesan to a salad, opt for a lighter dressing. This approach allows you to enjoy the cheese’s nutritional benefits, such as its protein and calcium content, without exceeding your daily calorie or fat limits. Balancing indulgence with moderation is the key to making Parmesan a healthy addition to your diet.
Finally, alternatives and substitutions can aid in portion control. If you find it difficult to limit Parmesan intake, consider mixing it with lower-calorie cheeses or using nutritional yeast, which provides a similar umami flavor with fewer calories and fat. This way, you can still enjoy the taste while keeping your overall calorie and fat consumption in check. Portion control isn’t about deprivation but about making informed choices to maintain a healthy and balanced diet.
Cheese Pizza: A Pregnancy Superfood?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Parmesan cheese can be a healthy addition when consumed in moderation. It is rich in nutrients like calcium, protein, and phosphorus, which support bone health and muscle function. However, it is also high in sodium and saturated fat, so portion control is key.
Yes, Parmesan cheese offers several nutritional benefits. It is an excellent source of calcium, which is essential for strong bones and teeth. It also contains vitamins A, B12, and zinc, which support immune function and overall health.
Parmesan cheese can be included in a weight-loss diet due to its high protein content, which helps promote satiety and reduces overall calorie intake. However, its high calorie and fat content means it should be consumed in small amounts as part of a balanced diet.
While Parmesan cheese is nutritious, excessive consumption can pose health risks due to its high sodium and saturated fat content. High sodium intake can lead to hypertension, while excessive saturated fat may increase the risk of heart disease. Individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies should also avoid it.











































