Cheddar cheese, a beloved staple in many cuisines, is a versatile dairy product that comes in various flavors and textures. While it is known for its rich, creamy taste, cheddar's nutritional profile is often overlooked. One aspect of nutrition that stands out is its fiber content, which is surprisingly low. Understanding the fiber content in cheddar cheese can be essential for those following specific dietary plans or aiming to meet their daily fiber requirements. This paragraph will delve into the question of how much fiber is present in cheddar cheese and explore the factors that influence its fiber content.
What You'll Learn

Cheddar Cheese: A Nutritional Overview
Cheddar cheese, a beloved dairy product with a rich history, is a staple in many cuisines worldwide. While it is renowned for its creamy texture and distinct flavor, it's also a nutrient-dense food that offers several health benefits. One aspect of nutrition that often receives attention is fiber content, an essential component of a balanced diet. However, cheddar cheese, like many dairy products, is not typically associated with being a significant source of dietary fiber.
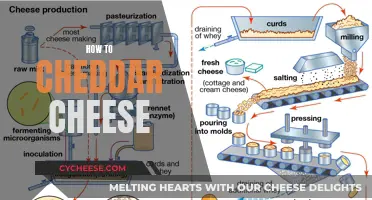
In terms of fiber, cheddar cheese generally contains a minimal amount. On average, a 100-gram serving of cheddar cheese provides less than 1 gram of dietary fiber. This is primarily due to the cheese-making process, which involves curdling milk and separating the curds and whey. The curds, which are the solid part of the milk, are then pressed and aged to produce cheddar cheese. During this process, much of the original milk components, including fiber, are concentrated and preserved in the final product.
The low fiber content in cheddar cheese can be attributed to the nature of milk itself. Milk, whether from cows, goats, or sheep, is relatively low in fiber. It primarily contains proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in the form of lactose (milk sugar). When cheese is made, the lactose is partially broken down, but the overall fiber content remains minimal. This is why cheddar cheese, despite being a good source of protein and calcium, is not considered a significant source of dietary fiber.
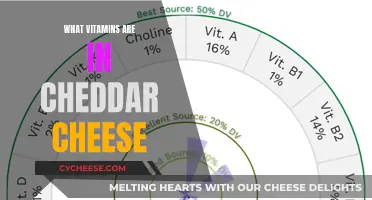
However, it's worth noting that while cheddar cheese may not be high in fiber, it still offers other nutritional benefits. It is an excellent source of protein, providing essential amino acids necessary for muscle growth and repair. Cheddar cheese also contains a good amount of calcium, which is vital for bone health and dental well-being. Additionally, it can be a source of vitamins A, B12, and D, depending on the specific variety and how it is produced.
For individuals following a high-fiber diet or those with specific dietary requirements, cheddar cheese may not be the primary source of fiber they seek. However, it can still be a part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. Combining cheddar cheese with high-fiber foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can contribute to a more comprehensive and nutritious meal. As with any food, moderation and a varied diet are key to maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
A Cheesy Twist: Cheddar's Gritty Comfort Food Delight
You may want to see also

Fiber Content in Cheddar: A Comparison
Cheddar cheese, a beloved staple in many cuisines, is renowned for its rich flavor and creamy texture. However, when it comes to nutritional content, cheddar's fiber content is often overlooked. The fiber in cheddar cheese is primarily found in the form of lactose, a natural sugar, and some soluble fibers. While cheddar is not typically associated with being a high-fiber food, it does contribute a small amount of dietary fiber to one's diet.
On average, a 100-gram serving of cheddar cheese contains approximately 0.1-0.2 grams of dietary fiber. This amount might seem insignificant, but it can still contribute to an individual's daily fiber intake, especially for those who consume it regularly. The fiber in cheddar is mainly derived from the milk's lactose content, which is broken down during the cheese-making process, releasing simple sugars and contributing to the cheese's characteristic tang.
Comparatively, cheddar's fiber content is relatively low compared to other cheese varieties and many plant-based sources of fiber. For instance, a similar serving of mozzarella cheese contains around 0.1 grams of fiber, while a plant-based source like broccoli provides approximately 2.6 grams of fiber per 100 grams. However, it's important to note that cheddar's low fiber content doesn't diminish its nutritional value. Cheddar is an excellent source of protein, calcium, and vitamins, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
The fiber in cheddar cheese is not easily digestible due to its low solubility, which means it may not significantly impact blood sugar levels. This characteristic also contributes to the cheese's creamy texture and long shelf life. Despite its modest fiber content, cheddar remains a popular choice for snacking, cooking, and adding flavor to various dishes.
In summary, while cheddar cheese is not a significant source of dietary fiber, it still offers a small but valuable contribution to one's fiber intake. When compared to other foods, cheddar's fiber content is modest, but it is part of a well-rounded nutritional profile that includes essential vitamins and minerals. Understanding the fiber content in cheddar can help individuals make informed dietary choices, especially for those aiming to increase their fiber intake through diverse food sources.
Cholesterol-Free Cheddar: Unveiling the Secret to Heart-Healthy Cheesing
You may want to see also

Cheddar's Fiber: Health Benefits and Sources
Cheddar cheese, a beloved dairy product, is a good source of protein and calcium, but it is not typically associated with fiber. However, the fiber content in cheddar can vary depending on several factors, including the type of milk used, the aging process, and the specific production methods. Understanding the fiber content in cheddar cheese can be an important aspect of a balanced diet, especially for those aiming to increase their fiber intake.
The fiber in cheddar cheese primarily comes from the milk's carbohydrate content, which is converted into lactose during the cheese-making process. While cheddar is not as high in fiber as some plant-based foods, it can still contribute to an individual's daily fiber requirement. On average, a 100-gram serving of cheddar cheese contains around 0.5-1 gram of fiber. This amount may seem small, but it can be beneficial for those who struggle to meet their fiber goals through other means.
The health benefits of fiber are well-documented. It promotes digestive health by preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. A diet rich in fiber can also help lower cholesterol levels, regulate blood sugar, and contribute to a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management. For individuals who are lactose intolerant or have a sensitivity to dairy, the fiber content in cheddar can be particularly useful, as it can be derived from lactose-free sources.
To increase the fiber content in your cheddar cheese, consider the following: Opt for aged cheddar, as the aging process can slightly increase the cheese's fiber content. Choose full-fat cheddar, as the fat content can enhance the absorption of certain nutrients, including fiber. Additionally, look for organic or grass-fed milk-based cheddars, as these may have higher-quality fats and potentially more beneficial nutrients.
Incorporating cheddar cheese into a balanced diet can be a simple way to boost fiber intake. For those who enjoy cheese, it can be a tasty and satisfying addition to meals. However, it's important to remember that fiber is just one aspect of a healthy diet, and a variety of whole foods should be consumed to ensure all nutritional needs are met.
Mid Cheddar's Origin: American Cheese or Not?
You may want to see also

Cheddar Cheese and Dietary Fiber
Cheddar cheese, a beloved dairy product, is a staple in many cuisines and is known for its rich flavor and creamy texture. While it is a popular ingredient in various dishes, it is not typically associated with being a significant source of dietary fiber. However, understanding the fiber content in cheddar cheese can be an essential aspect of nutrition, especially for those following specific dietary plans or managing their fiber intake.
The dietary fiber content in cheddar cheese is generally quite low. On average, a 100-gram serving of cheddar cheese contains less than 1 gram of dietary fiber. This is because cheese, in general, undergoes a process of curdling and straining, which removes much of the milk's natural fiber-rich components. The final product, cheddar cheese, is often a concentrated source of protein and fat, with minimal fiber. For context, a similar serving of whole milk, from which cheese is derived, contains around 0.1 grams of fiber, indicating that the majority of the fiber is lost during the cheese-making process.
Despite its low fiber content, cheddar cheese can still be a valuable addition to a balanced diet. It is an excellent source of calcium, which is crucial for bone health, and it also provides a good amount of protein. Additionally, cheese contains some essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin B12 and phosphorus. For individuals aiming to increase their fiber intake, it is recommended to focus on other food groups, such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, which are naturally rich in dietary fiber.
For those on a low-fiber diet or suffering from digestive issues, cheddar cheese can be consumed in moderation. The low fiber content makes it easier to digest and less likely to cause discomfort. However, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate dietary choices based on individual health needs and conditions.
In summary, cheddar cheese is not a significant source of dietary fiber, with a 100-gram serving typically containing less than 1 gram. While it offers other nutritional benefits, such as protein and calcium, individuals seeking to increase their fiber intake should focus on whole, fiber-rich foods. Cheddar cheese can be a part of a balanced diet, but it should be consumed in moderation, especially for those with specific dietary requirements.
Unveiling the Secrets of Baby Cheddar: A Delicious Journey
You may want to see also

Cheddar's Fiber: Impact on Digestion and Health
Cheddar cheese, a beloved dairy product, is known for its rich flavor and creamy texture, but it's not typically associated with fiber. However, cheddar cheese does contain a small amount of dietary fiber, which can have several benefits for your digestive system and overall health. Understanding the fiber content in cheddar cheese and its impact on digestion can provide valuable insights for those seeking to improve their dietary habits.
The fiber in cheddar cheese primarily comes from the natural ingredients used in its production, such as milk, cultures, and enzymes. While the fiber content may not be as high as in plant-based foods, it still contributes to the overall nutritional value of the cheese. On average, a 100-gram serving of cheddar cheese contains around 0.5-1 gram of fiber, which is relatively low compared to other food sources. However, this small amount of fiber can still have a positive effect on digestion.
Fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. It acts as a bulking agent, adding bulk to your stool and promoting regular bowel movements. This can help prevent constipation and promote a healthy gut. Additionally, fiber can support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which play a crucial role in overall health. Cheddar cheese, with its moderate fiber content, can contribute to a balanced diet that supports digestive well-being.
For individuals with specific dietary needs, cheddar cheese's fiber content can be particularly beneficial. Those following a low-carb or ketogenic diet may find that the fiber in cheese helps to add bulk to meals, providing a sense of fullness and satisfaction. Moreover, the fiber in cheddar cheese can help slow down the absorption of fat, which may aid in weight management and overall health.
Incorporating cheddar cheese into a balanced diet can be a simple way to increase fiber intake. While the fiber content may not be as high as in whole grains or legumes, it still offers digestive benefits. It is worth noting that the fiber in cheese is not as easily digestible as in other food sources, so moderation is key. Combining cheddar cheese with high-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can create a well-rounded diet that supports both digestion and overall health.
Kraft Cheddar Cheese: Keto-Friendly or Not? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Cheddar cheese is not a significant source of dietary fiber. It is primarily composed of protein and fat, with very little fiber content. A 100-gram serving of cheddar cheese typically contains less than 1 gram of fiber.
The fiber content in cheese, including cheddar, is generally low because cheese is made by curdling milk and separating the curds (solid part) from the whey (liquid part). The curds are then pressed and aged, which removes most of the water and any remaining fiber.
While cheddar cheese is not high in fiber, it does offer other nutritional benefits. It is a good source of protein, calcium, and vitamins like vitamin A and vitamin B12. These nutrients are essential for bone health, muscle function, and overall well-being.
Cheddar cheese itself is not a significant source of dietary fiber, but it can be part of a balanced diet that includes other fiber-rich foods. Consuming a variety of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes can help meet daily fiber requirements.
Some cheese varieties, like Swiss cheese or mozzarella, may have slightly higher fiber content compared to cheddar due to differences in production methods and milk composition. However, the overall fiber content in cheese is generally low, and it is not a primary source of dietary fiber.