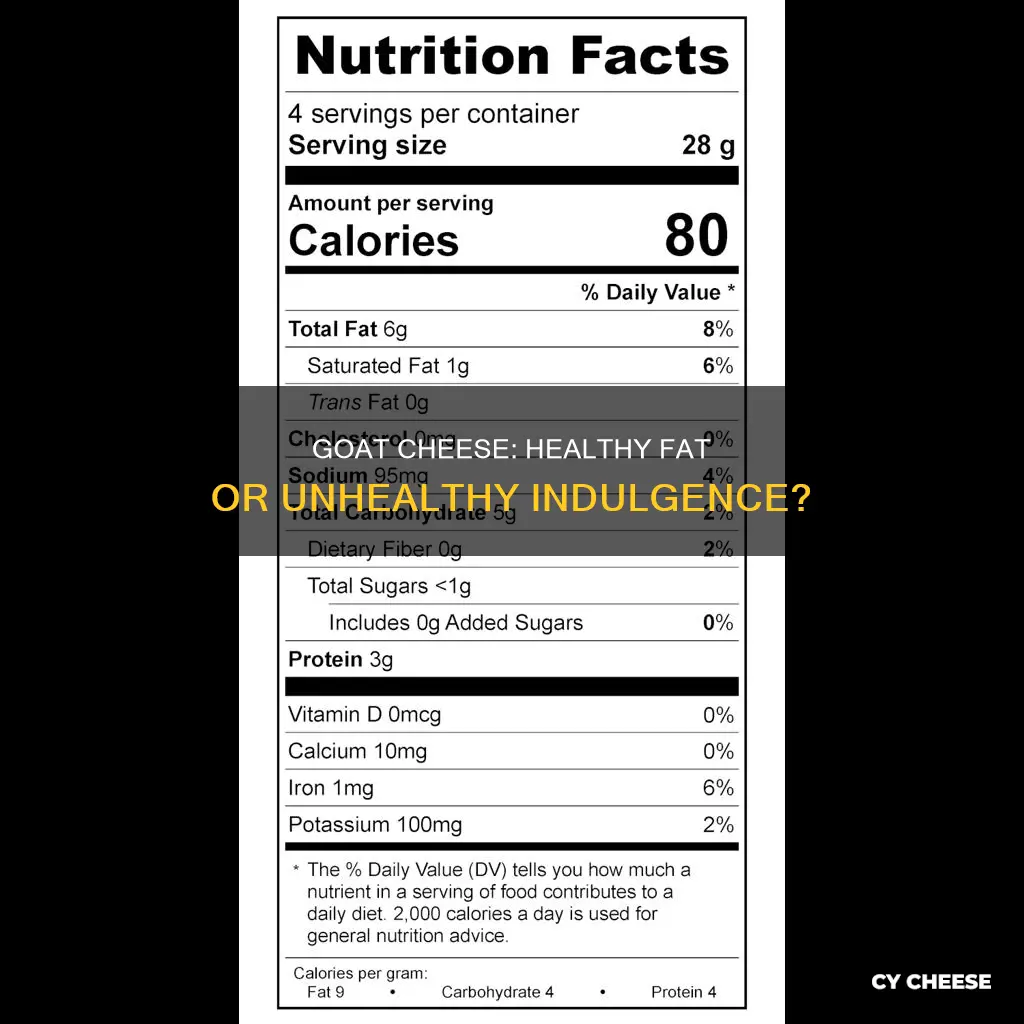
Goat cheese is a popular ingredient in many dishes, from salads to pasta. But is it a healthy fat? Goat cheese is a source of healthy fats, protein, calcium, phosphorus, copper, vitamins B and D, and probiotics. It is also lower in lactose and calories than regular cheese, making it a healthier option for those watching their calorie intake. Goat cheese has anti-inflammatory properties and may be easier to digest than cow's milk cheese, especially for those with lactose intolerance. However, it is still high in fat and should be consumed in moderation to avoid weight gain.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Healthy fats | Yes, goat cheese is a source of healthy fats, including capric acid, a medium-chain fatty acid with anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. It also contains omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid, a potential antioxidant. |
| Calcium | Goat cheese is high in calcium, an essential nutrient for bone, teeth, and organ health. |
| Selenium | Goat cheese is a good source of selenium, a trace mineral that helps the body break down DNA-damaging peroxides, reducing the risk of cancer, thyroid disease, and cardiovascular disease. |
| Probiotics | Goat cheese contains beneficial probiotics, a type of healthy bacteria that can improve immune system function and reduce vulnerability to illness. |
| Protein | Goat cheese provides protein, which, along with calcium and iron, supports bone formation and mineral absorption. |
| Vitamins | Goat cheese contains vitamins A, B, and D, as well as B vitamins like vitamin B6. |
| Minerals | Goat cheese provides phosphorus, copper, and iron. Copper is important for maintaining energy levels and plays a role in skeletal health, hormone production, and red blood cell production. |
| Digestibility | Goat cheese is easier to digest than cow's milk cheese due to its smaller fat molecules and lower lactose content. This makes it a good alternative for those with lactose intolerance or sensitive stomachs. |
| Calories | Goat cheese typically has fewer calories than regular cheese, making it a healthier option for calorie-conscious individuals. |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn
- Goat cheese is a good source of healthy fats, protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals
- It has fewer calories and fats than regular cheese, making it a healthier option
- Goat cheese is easier to digest than cow's milk cheese, with lower lactose content
- Goat cheese contains probiotics, which improve immune function and reduce illness risk
- It is a good source of selenium, a trace mineral that helps to prevent cancer and cardiovascular disease

Goat cheese is a good source of healthy fats, protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals
Goat cheese is a nutritious food that offers a range of health benefits. It is a good source of healthy fats, protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals, which can contribute to a well-rounded diet.
Firstly, goat cheese contains healthy fats, including capric acid, a medium-chain fatty acid with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. These beneficial fatty acids can promote gut and immune health, and may even offer some protection against certain diseases. While goat cheese does contain saturated fat, this has been subject to some debate, with the "French Paradox" demonstrating that high consumption of saturated fat from cheese and butter does not necessarily lead to higher rates of heart disease.
Goat cheese is also an excellent source of calcium, an essential mineral for bone, teeth, and skeletal health. Calcium helps to prevent osteoporosis and other bone disorders, and just one or two servings of goat cheese can provide about 10-30% of your daily calcium needs. In addition to calcium, goat cheese contains phosphorus, which is the second most abundant element in the human body and also plays a role in bone health.
Goat cheese is also a good source of protein, which, alongside calcium and iron, may support bone formation and mineral absorption. It also contains B vitamins, including vitamin B6, and some iron, which can contribute to overall health and energy levels. Goat cheese is lower in lactose than regular cheese, making it easier to digest and a good alternative for those with sensitive stomachs or lactose intolerance.
Finally, goat cheese contains probiotics, healthy bacteria that can improve immune function and reduce vulnerability to illness. It is also a source of selenium, a trace mineral that helps the body break down DNA-damaging peroxides, potentially lowering the risk of cancer, thyroid disease, and cardiovascular disease.
Goat Cheese: Why Does It Smell So Bad?
You may want to see also

It has fewer calories and fats than regular cheese, making it a healthier option
Goat cheese is a healthy fat that has multiple benefits over regular cheese. It has a unique tangy flavour and creamy texture, making it a tasty addition to a variety of dishes.
Goat cheese is a good source of healthy fats, protein, calcium, phosphorus, copper, B vitamins, and iron. Calcium is essential for bone and dental health, and the combination of calcium, protein, and iron may help with bone formation and mineral absorption. Copper is important for maintaining high energy levels, and phosphorus is the second most abundant element in the human body, playing a role in skeletal health and hormone production.
Goat cheese also contains capric acid, a beneficial medium-chain fatty acid with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. It may also contain heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid, a potential antioxidant.
Compared to regular cheese, goat cheese typically has fewer calories and fats, making it a healthier option for those watching their calorie intake. It is also lower in lactose and easier to digest, which can be beneficial for people with lactose intolerance or sensitive stomachs.
However, it's important to remember that goat cheese should be consumed in moderation to avoid weight gain, and that a balanced diet is essential for a healthy lifestyle.
Goat Cheese and Eggplant: A Japanese-Inspired Culinary Adventure
You may want to see also

Goat cheese is easier to digest than cow's milk cheese, with lower lactose content
Goat cheese is a healthy fat that is easier to digest than cow's milk cheese. It has a lower lactose content, making it a good alternative for those with lactose intolerance or sensitive stomachs. The smaller fat molecules in goat cheese also contribute to its better digestibility.
Goat cheese is a good source of healthy fats, including capric acid, a medium-chain fatty acid with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. It may also contain heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid, a potential antioxidant. While goat cheese is high in fat, it contains less fat than cheeses made from cow's milk. It is also lower in sugar and carbs, with only about one gram per serving.
In addition to healthy fats, goat cheese provides several other important nutrients. It is a good source of calcium, which is essential for bone, teeth, and organ health. Goat cheese also contains phosphorus, copper, B vitamins, and iron. The combination of protein, calcium, and iron may support bone formation and mineral absorption. Furthermore, goat cheese is a source of probiotics, which can improve immune function and reduce the risk of illness.
The exact nutrient composition of goat cheese can vary depending on factors such as the breed of goat, country of origin, time of year, and aging process. However, overall, goat cheese is a healthy option that is easier to digest than cow's milk cheese due to its lower lactose content and smaller fat molecules. It offers a range of nutrients and can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet.
Goat Cheese: High in Saturated Fats?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Goat cheese contains probiotics, which improve immune function and reduce illness risk
Goat cheese is a nutritious dairy product that offers a range of health benefits. Notably, it contains beneficial probiotics, which are a type of healthy bacteria. Probiotics play a crucial role in improving immune function and reducing the risk of illness.
Probiotics found in goat cheese colonize the intestines, where they compete with any unhealthy bacteria or pathogens present. This colonization helps to improve the effectiveness of the immune system. By reducing the presence of harmful bacteria and supporting the growth of healthy bacteria, probiotics contribute to a stronger immune response and lower the chances of falling ill.
Goat cheese is also a good source of calcium, an essential mineral for maintaining strong bones, teeth, and organ health. A diet rich in calcium can help prevent osteoporosis and other bone disorders later in life. Additionally, goat cheese contains selenium, a trace mineral that aids in breaking down DNA-damaging peroxides, thereby lowering the risk of certain diseases, including cancer, thyroid issues, and cardiovascular problems.
The presence of probiotics in goat cheese is particularly noteworthy due to their positive impact on digestive health. Probiotics aid in the breakdown of food, reduce inflammation in the gut, and support the growth of beneficial bacteria. This can be especially advantageous for individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy sensitivities, as goat cheese naturally contains lower levels of lactose and A1 casein, a type of protein that can cause digestive issues.
In addition to its probiotic content, goat cheese provides healthy fats, including medium-chain fatty acids like capric acid, which has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. These healthy fats can improve satiety, aiding in weight loss, and may offer additional health benefits such as lowering the risk of certain types of acne. Overall, incorporating goat cheese into one's diet can be a delicious and nutritious way to boost immune function and support overall health.
Goat Cheese Kosher for Passover: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

It is a good source of selenium, a trace mineral that helps to prevent cancer and cardiovascular disease
Goat cheese is a good source of selenium, an essential trace mineral more commonly found in seafood. Selenium is a powerful antioxidant that helps to prevent cancer and cardiovascular disease by reducing the risk factors associated with these diseases.
Selenium is a vital component of our body's antioxidant defence system, helping to neutralise harmful free radicals and protecting our cells from damage. It also plays a role in regulating thyroid function and boosting the immune system. As an antioxidant, selenium helps to prevent the oxidation of cholesterol, reducing the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries and lowering the likelihood of heart disease.
In addition to its role in preventing cardiovascular disease, selenium is also known for its cancer-protective properties. Studies have shown that selenium can inhibit the growth and spread of cancer cells, particularly in the bladder, breast, lung, and digestive system. Selenium may also enhance the effectiveness of certain cancer treatments.
Goat cheese, being a good source of selenium, can help to ensure adequate intake of this important mineral. However, it is important to consume goat cheese in moderation as part of a balanced diet, as it can also be high in fat.
Goat Cheese: Sweet or Savory?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Goat cheese has several health benefits and can be consumed as part of a healthy diet. It is a good source of calcium, healthy fats, protein, phosphorus, copper, B vitamins, and iron. It also contains probiotics and has anti-inflammatory properties.
Goat cheese is a good source of calcium, an essential nutrient for bone health. Consuming adequate calcium can help prevent osteoporosis and other bone disorders later in life. Additionally, the combination of protein, calcium, and copper in goat cheese may support bone formation and mineral absorption.
Yes, goat cheese contains healthy fats, including capric acid, a medium-chain fatty acid with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. It may also contain heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid, a potential antioxidant.
Goat cheese is generally considered a healthier alternative to cow's milk cheese. It has lower lactose content, making it easier to digest, especially for those with lactose intolerance. Goat cheese also typically has fewer calories and less fat than cow's milk cheese.
While goat cheese offers nutritional benefits, it should still be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. It is high in fat, particularly saturated fat, so excessive intake may contribute to weight gain. Additionally, despite its lower lactose content, those with severe lactose intolerance should still exercise caution when consuming goat cheese.










































