Cheese is often considered unhealthy, and many people cut it out of their diets when trying to lose weight. However, eating cheese can have several health benefits, and it can be a great source of protein and calcium. But is it healthy to eat for breakfast? This paragraph will explore the nutritional value of cheese and discuss whether or not it is a good breakfast option.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
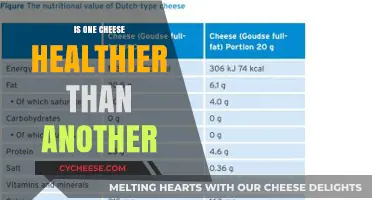
| Nutritional Value | Cheese contains over 50 vitamins, minerals, and trace nutrients, including B vitamins, zinc, phosphorus, vitamin B12, and vitamin A. It is also a good source of protein and calcium. |
| Weight Loss | While some people cut cheese from their diet when trying to lose weight, low-fat cheeses and those made from goat's or cow's milk can be part of a weight-loss diet. Studies have also shown that eating higher-calcium cheese may protect against obesity. |
| Oral Health | The presence of probiotics and other components in cheese may positively affect oral health by reducing cavities and encouraging remineralization. |
| Heart Health | Cheese contains saturated fats, which have been linked to an elevated risk of heart disease. However, one study found that consuming full-fat cheese reduced total cholesterol and "bad" LDL cholesterol. Additionally, individuals who regularly consume dairy have a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. |
| Sodium Content | Cheese can be high in sodium, with one slice of cheddar cheese containing about 180 mg of sodium. Lower-sodium cheeses are available for those watching their sodium intake. |
| Lactose Content | Aged and hard cheeses are naturally low in lactose, making them suitable for people with lactose intolerance. |
Explore related products
$1.39
What You'll Learn

Cheese is a good source of protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals
Eating a piece of cheese for breakfast can be healthy, as cheese is a good source of protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals.
Protein is essential for muscle growth and maintenance, and cheese is a great source of high biological value protein. For example, low-fat cottage cheese provides 24 grams of protein per cup (220 grams), making it a filling breakfast option. Other types of cheese that are good sources of protein include Swiss cheese and goat cheese.
Cheese is also rich in calcium, which is important for bone and dental health. Blue cheese, for instance, provides 11% of the daily recommended amount of calcium in just one slice. Soft cheeses, such as cottage cheese, are also good sources of calcium, providing 80 milligrams of calcium in a half-cup serving.
Cheese contains over 50 vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins, which help maintain healthy skin, and fat-soluble vitamins, which contribute to lustrous hair. Other vitamins and minerals found in cheese include zinc, phosphorus, vitamin B12, and vitamin A, which boost the immune system and support eye health.
When incorporating cheese into your breakfast, it is important to consider the type of cheese and how it is consumed. Some cheeses are lower in fat and calories, such as goat cheese and feta, while others are naturally high in saturated fat and sodium, such as blue cheese. To maximize the health benefits of cheese, pair it with nutritious, high-fiber foods such as whole grain bread, fruits, or vegetables, instead of refined grains and processed meats.
White vs Yellow Cheese: Which is Healthier?
You may want to see also

Some cheeses may contain beneficial probiotics
Cheese is a nutritious food that can be a great addition to breakfast. It provides ample amounts of protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals. However, it is typically high in calories, saturated fat, and sodium, so it should be consumed in moderation.
Some varieties of cheese may contain beneficial probiotics, which are good bacteria that can contribute to gut and overall health. Probiotics are typically found in cheeses that have been aged but not heated afterward, as heat can kill the bacteria. These include both soft and hard cheeses such as Swiss, provolone, Gouda, cheddar, Edam, Gruyère, cottage cheese, and blue cheeses like Stilton. Eating foods with probiotics, like cheese, can help restore the balance of good bacteria in the gut, which may be linked to improved gut health, reduced allergies, better mood, and decreased arthritis symptoms.
When selecting a cheese with probiotics, look for those that have not been heated after aging. Additionally, check the labels for "live cultures" to ensure the presence of probiotics. For example, cottage cheese often contains live cultures, but it's important to confirm this on the label.
It's worth noting that other probiotic food options include dairy-free yogurt, kefir, kombucha, sauerkraut, miso, tempeh, and kimchi. Probiotic foods have the potential to provide significant health benefits, but they are just one part of a larger picture that includes a diverse and plant-rich diet.
Burgers: Meat vs. Meat and Cheese, Which is Healthier?
You may want to see also

Cheese may have a positive impact on oral health
While cheese is often cut from diets in the name of weight loss, it is a great health food with several nutritional benefits. One piece of cheese for breakfast can be healthy, depending on the type of cheese and what it is paired with.
Secondly, cheese is rich in calcium and phosphorus, which strengthen teeth and bones. These minerals also seem to be a factor in the cariostatic mechanism of cheese, helping to reduce enamel demineralization.
Thirdly, cheese contains casein, a protein that creates a protective film over teeth. This acts as a shield against acid damage, especially after eating something acidic like citrus fruit or sugary foods.
Finally, cheese can alter the mouth's pH, creating an alkaline environment that helps to neutralise the acids produced by harmful bacteria. This, again, reduces the risk of enamel erosion and cavities.
To balance out the potential for dry mouth caused by the fats in cheese, it is recommended to eat cheese with fibrous foods like apples or celery.
Healthy Breakfast: Scrambled Eggs and Mozzarella Cheese
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Cheese can be part of a weight-loss diet if consumed in moderation
Cheese is often associated with high fat and salt content, and many people cut it out of their diets when trying to lose weight. However, cheese can be part of a weight-loss diet if consumed in moderation. It is a good source of protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals, providing many health benefits.
Cheese contains over 50 vitamins, minerals, and trace nutrients. B vitamins help maintain healthy skin, while fat-soluble vitamins contribute to healthy hair. Zinc, phosphorus, Vitamin B12, and Vitamin A boost the immune system, and high amounts of antioxidant nutrients help prevent free radical damage and cell mutations, slowing down the ageing of cells. Studies have also shown that Conjugated Linoleic Acid, found in cheese, may help prevent the formation of tumour cells and metastasis of cancer cells.
Low-fat cottage cheese is a high-protein breakfast option, providing 24 grams of protein per cup (220 grams). It is also filling, and studies have found it to be as satisfying as eggs. Cottage cheese is also high in fibre and complex carbohydrates, which digest slowly, helping you feel full for longer, and are less likely to raise blood sugar levels.
Goat's milk cheese contains the least amount of fat, followed by cow's milk and then buffalo milk cheese. So, when trying to lose weight, it is best to opt for low-fat cheeses, such as low-fat cheddar, and to be mindful of portion sizes.
In summary, cheese can be a nutritious part of a weight-loss diet, offering many health benefits, but it should be consumed in moderation, and low-fat options should be prioritised.
Chopped Cheese: Healthy or Unhealthy?
You may want to see also

Low-fat cheeses are a healthier option
Cheese is a nutritious food, packed with protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals. However, it is often cut from diets due to its high fat and calorie content. Nevertheless, some low-fat cheeses are not only healthier but also provide the same nutrients as full-fat varieties.
Low-fat cheeses are defined as containing no more than 1 gram of saturated fat per serving by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). These cheeses include non-fat and low-fat versions of popular cheeses like cheddar, Swiss, cottage, ricotta, and mozzarella. Goat's cheese is also a low-calorie option, though it is relatively high in fat compared to other low-fat cheeses.
To make your breakfast healthier, consider swapping out high-fat cheeses for low-fat options. For instance, a sandwich with a slice of low-fat cheddar on whole wheat bread with veggie slices is a nutritious and tasty option. You can also pair low-fat cottage cheese with whole wheat toast or blend it into a smoothie for a filling breakfast.
Cheese and Heating: Healthy or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, eating one piece of cheese for breakfast can be healthy. Cheese is a good source of protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals. It also contains probiotics, which can positively impact oral health. However, it's important to choose the right type of cheese, as some are high in fat and sodium.
Cheese is a nutritious food that can provide you with a good amount of protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals. It may also offer oral health benefits due to its probiotics content. Additionally, some studies suggest that eating cheese may help reduce the risk of obesity, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes.
There are several healthy ways to incorporate cheese into your breakfast:
- Pair low-fat cottage cheese or Greek yogurt with fruits or whole wheat toast.
- Make a grilled cheese sandwich with low-fat cheddar or gouda on whole wheat bread.
- Add cheese to an egg sandwich or a vegetable omelette.
- Top oatmeal or a bagel with a semi-soft cheese like Saint-Paulin.