Cheese is a staple food in many cultures and is produced by adding acid or bacteria to the milk of various animals and then ageing or processing the solid parts of the milk. It is rich in essential nutrients, such as amino acids, protein, fatty acids, and vitamins and minerals. However, some people are concerned that cheese is high in fat, sodium, and calories. In this context, is unprocessed cheese healthy?
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Nutritional benefits | Cheese is rich in essential nutrients, including amino acids, protein, fatty acids, vitamins and minerals. |
| Health benefits | Cheese may help prevent heart disease and osteoporosis. |
| Drawbacks | Cheese is high in fat, sodium, and calories. |
| Best choices | Mozzarella, blue cheese, feta, quark, ricotta, mascarpone, cheddar, Swiss cheese, Roquefort, goat cheese, Parmesan. |
Explore related products
$17.38 $19.95
What You'll Learn

Unprocessed cheese is a good source of protein, vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids
Cheese is a dairy product that is made from milk and milk products. It is a rich source of essential nutrients, including amino acids, protein, fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. However, not all cheeses provide the same nutritional benefits.
Some unprocessed cheeses are also rich in vitamins. Cheddar cheese, for instance, is high in vitamin K, which is good for heart health and can reduce the chances of bone fractures and cancer risk. Goat cheese is a good source of vitamin A, which is important for eye health.
Unprocessed cheese can also be a good source of minerals. Parmesan, for example, is rich in calcium and phosphorus, which play a role in bone formation and may promote bone health. Feta cheese is also a source of phosphorus and calcium, which are important for bone and dental health.
In summary, unprocessed cheese can be a good source of protein, vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids. However, it is important to remember that not all cheeses provide the same nutritional benefits, and it is always best to consume cheese in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Farmer Cheese: Healthy Heart Superfood?
You may want to see also

It can be high in fat, sodium, and calories
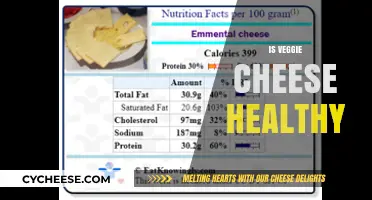
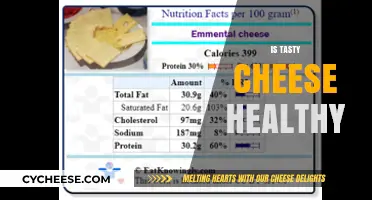
Cheese is a dairy product that comes in hundreds of textures and flavours. It is produced by adding acid or bacteria to the milk of various animals and then ageing or processing the solid parts of the milk. While cheese is rich in essential nutrients, it can also be high in fat, sodium, and calories.
Cheese is a good source of protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals. Eating cheese may help prevent osteoporosis and heart disease. However, some types of cheese are high in fat, sodium, and calories. For example, mascarpone is one of the highest-fat cheeses, with 44% fat content, of which 30% is saturated. Goat cheese is also high in fat, with around 20% fat content, although the fat globules are smaller, which facilitates digestion.
Some cheeses are also high in sodium, which can contribute to high blood pressure and heart disease. Blue cheese, feta, and goat cheese are examples of cheeses that are high in sodium. If you are on a low-sodium diet, it is important to consider the sodium content of cheese.
In addition, some cheeses are high in calories. While mozzarella is relatively low in calories, other cheeses, such as cheddar, have higher calorie content. It is important to consider the calorie content when choosing a cheese, especially if you are watching your calorie intake.
Overall, while cheese is a nutritious food, it is important to consume it in moderation. The specific type of cheese and its method of production can affect its nutritional content. When choosing a cheese, consider its fat, sodium, and calorie content to make a healthier choice.
Roumy Cheese: Healthy or Not?
You may want to see also

It can be healthy in moderation
Cheese is a dairy product that is made from milk and milk products, and it comes in hundreds of textures and flavours. It is rich in essential nutrients, such as amino acids, protein, fatty acids, and vitamins and minerals. However, some people are concerned that cheese is high in fat, sodium, and calories.
In moderation, cheese can be a perfectly acceptable food to enjoy. It can be a good source of protein, calcium, and several other nutrients. Eating cheese may even help prevent heart disease and osteoporosis.
Some cheeses are healthier than others. For example, mozzarella is lower in sodium and calories than most other cheeses. It also contains bacteria that act as probiotics, which may improve gut health and regularity, promote immunity, and decrease inflammation.
Another healthy option is goat cheese, which contains more protein and higher amounts of niacin, calcium, iron, and potassium than cow's milk cheese. Goat cheese is also a rich source of vitamin A, which is important for eye health. Feta, ricotta, Swiss cheese, and Parmesan are also good choices, as they are naturally lower in sodium.
When choosing between low-fat and full-fat cheese, it is generally recommended to go for full-fat. Low-fat cheeses have been stripped of their beneficial fats and often contain artificial additives to mimic the texture of full-fat varieties. However, it is important to consume full-fat cheese in moderation, as part of a balanced diet.
Liquid Cheese: Healthy or Unhealthy?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Raw, unpasteurised cheese has more beneficial enzymes and nutrients
Cheese is a dairy product that comes in hundreds of textures and flavours. It is produced by adding acid or bacteria to the milk of various animals and then ageing or processing the solid parts of the milk. Cheese is rich in essential nutrients, including amino acids, protein, fatty acids, and vitamins and minerals. However, it is also high in fat, sodium, and calories, which has led to concerns about its healthiness.
Some cheeses are healthier than others, and some are lower in calories and fat. For example, mozzarella is lower in sodium and calories than most other cheeses, and feta is lower in fat. Quark, a soft, fresh cheese, is virtually fat-free and has no added salt. Ricotta is another healthier option, as it contains less salt and fat.
Raw, unpasteurised cheese has been touted by some as a healthier option due to its higher content of beneficial enzymes and nutrients. Pasteurisation is the process of heating milk to a high temperature to kill bacteria, which can also destroy beneficial microbes in milk that are good for the human gut. Proponents of raw cheese argue that it contains more beneficial bacteria, fatty acids, proteins, vitamins, enzymes, and rich flavours. They believe that these compounds make it a better choice for people with autoimmune disorders, allergies, asthma, lactose intolerance, and for anyone who wants a more nutritious food.
However, critics of raw cheese point out that pasteurisation has been effective in preventing people from getting seriously ill. There have been recent bacterial outbreaks linked to consuming cheese made from unpasteurised milk, and health authorities recommend avoiding raw milk or raw milk products. While raw cheese may offer some potential benefits, the nutritional advantages may not outweigh the increased risk of infection.
Cheese and Cholesterol: What's the Healthy Balance?
You may want to see also

Organic cheese is healthier due to higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids
Cheese is a dairy product that comes in hundreds of textures and flavours. It is produced by adding acid or bacteria to the milk of various animals and then ageing or processing the solid parts of the milk. Cheese is rich in essential nutrients, including amino acids, protein, fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. However, it is also high in fat, sodium, and calories.
Organic cheese is generally considered healthier than processed cheese. One reason for this is the higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids found in organic cheese, particularly those made from grass-fed or pasture-raised animal milk. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining a healthy heart, brain, and eyes. While cheese does contain small amounts of omega-3s, the levels can vary depending on the type of cheese and the diet of the animal whose milk is used.
Alpine cheese, for example, has been found to contain four times more linolenic acid (a type of omega-3) than cheddar, as well as higher total amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. This is because cows that graze on fresh alpine grass produce milk with higher levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fat. Similarly, yak cheese has been shown to have higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids when the yaks are fed diets enriched with omega-3 fatty acids.
While cheese can be part of a healthy diet, it is important to consume it in moderation due to its high-fat content. To meet the recommended daily intake of omega-3 fatty acids, it is best to focus on foods rich in eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), such as fatty fish, plant oils, nuts, seeds, and algae. These foods provide significantly higher amounts of omega-3s than cheese.
In conclusion, organic cheese may be considered healthier than processed cheese due to its higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, which offer important health benefits. However, it is important to note that cheese should be consumed in moderation and should not be relied upon as the sole source of omega-3s in one's diet.
Stracciatella Cheese: Healthy or Unhealthy?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Unprocessed cheese is rich in essential nutrients, such as amino acids, protein, fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. Eating cheese may help prevent heart disease and osteoporosis.
Some examples of unprocessed cheese include Parmesan, Roquefort, and raw-milk Brie or Camembert.
A serving of cheese is considered to be one ounce, or about the size of three standard dice. As with all foods, cheese should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.