American cheese is a processed cheese product made from several types of cheese and other ingredients. It is high in protein but also high in sodium and unsaturated fats. It is typically yellow or white in colour, and has a mild, creamy flavour and a medium-firm consistency. It was invented in the 1910s by James L. Kraft, the founder of Kraft Foods Inc.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type | Processed cheese |
| Ingredients | Cheddar, Colby, or similar cheeses, in conjunction with sodium citrate |
| Texture | Creamy |
| Flavour | Mild, salty |
| Consistency | Medium-firm |
| Melting point | Low |
| Colour | Yellow or white |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn
- American cheese is a processed cheese made from cheddar, Colby, or similar cheeses
- It is mixed with sodium citrate, which allows it to be pasteurised without separating
- It is typically yellow or white in colour
- Yellow American cheese is seasoned and coloured with annatto
- It is high in protein but also high in sodium and unsaturated fats

American cheese is a processed cheese made from cheddar, Colby, or similar cheeses
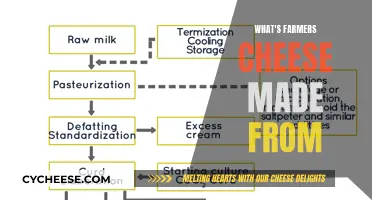
American cheese is a processed cheese made from a blend of several types of cheese, including cheddar, Colby, washed curd cheese, and granular cheese. It is also made with sodium citrate, which allows the cheese to be pasteurised without its components separating. This gives it a creamy texture and a low melting point. It is typically yellow or white in colour, with the yellow variety seasoned and coloured with annatto.
Processed American cheese was invented in the 1910s by James L. Kraft, the founder of Kraft Foods Inc. However, British colonists made cheddar cheese soon after their arrival in North America. American cheese is a common ingredient in classic American dishes such as cheeseburgers and grilled cheese sandwiches.
The cheese you find at the deli counter is usually made from real cheese, although it may not be wholly cheese, so check the label for the words "Pasteurized Process cheese". These deli cheeses still have fewer chemicals and extracts than the individually packaged stuff, so they will usually taste fresher and more flavourful.
White Cheese Dip: A Quick Guide to Its Ingredients
You may want to see also

It is mixed with sodium citrate, which allows it to be pasteurised without separating
American cheese is a processed cheese made from a blend of several types of cheese, including Cheddar, Colby, washed curd cheese, and granular cheese. It is mixed with sodium citrate, which allows it to be pasteurised without separating. This is what gives American cheese its smooth, creamy texture and prevents it from turning greasy when melted.
Sodium citrate is a salt derived from citric acid. It is commonly used as a food additive to enhance flavour and extend shelf life. In the case of American cheese, sodium citrate acts as an emulsifier, helping to keep the cheese's components evenly mixed and preventing separation during the pasteurisation process.
The addition of sodium citrate was a key innovation in the development of processed American cheese. James L. Kraft, the founder of Kraft Foods Inc., invented the process in the 1910s and obtained a patent for it in 1916. This method of cheese-making allowed for the creation of a product with a mild flavour, medium-firm consistency, and low melting point, making it ideal for use in classic American dishes such as cheeseburgers and grilled cheese sandwiches.
While the inclusion of sodium citrate has practical benefits for the production and use of American cheese, it also contributes to the product's high sodium content. This is one of the reasons why American cheese has gained a reputation for being of lower quality compared to natural cheeses.
Cheese Through the Ages: A Historical Perspective
You may want to see also

It is typically yellow or white in colour
American cheese is typically yellow or white in colour. Yellow American cheese is seasoned and coloured with annatto. The colour of American cheese may also range from white to light yellow or orange.
American cheese is a processed cheese made from several types of cheese and other ingredients. It is made by mixing one or more types of cheeses, including Cheddar cheese, washed curd cheese, Colby cheese, and granular cheese. It is mild with a creamy texture and salty flavour, has a medium-firm consistency, and has a low melting point.
The cheese you find at the deli counter is usually made from real cheese (it may not be wholly cheese, so check the label for the words “Pasteurized Process cheese”). These deli cheeses still have fewer chemicals and extracts than the individually packaged stuff, so they will usually taste fresher and more flavorful.
Processed American cheese was invented in the 1910s by James L. Kraft, the founder of Kraft Foods Inc., who obtained a patent for his manufacturing process in 1916.
Vegan Cheddar Cheese: What's in the Recipe?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Yellow American cheese is seasoned and coloured with annatto
American cheese is a processed cheese made from a blend of several types of cheese and other ingredients. It is typically yellow or white in colour; yellow American cheese is seasoned and coloured with annatto. It is mild with a creamy texture and salty flavour, and has a medium-firm consistency and a low melting point. It is typically sold in the form of solid blocks, shredded, cubes, spread, or individually wrapped slices commonly known as "singles".
Annatto is added to American cheese to give it a more appealing colour and to standardise the colour across different batches of cheese. The addition of annatto also helps to differentiate American cheese from other types of cheese, such as cheddar or Swiss cheese, which are typically white or light yellow in colour.
In addition to its use as a colouring agent, annatto also has some potential health benefits. It is a source of antioxidants, which can help to protect the body against damage caused by free radicals. Annatto also contains anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce inflammation in the body.
Explore Denmark's Cheese Specialties: A Cultural Delicacy
You may want to see also

It is high in protein but also high in sodium and unsaturated fats
American cheese is a processed cheese made from a blend of several types of cheese, including Cheddar, Colby, washed curd cheese, and granular cheese. It is high in protein but also high in sodium and unsaturated fats.
Processed American cheese was invented in the 1910s by James L. Kraft, the founder of Kraft Foods Inc. It is typically yellow or white in colour, with the yellow variety seasoned and coloured with annatto. It has a mild flavour and a creamy, smooth texture.
American cheese is a common ingredient in classic American dishes such as cheeseburgers and grilled cheese sandwiches. It is also often sold in solid blocks, shredded, cubes, spread, or individually wrapped slices.
The cheese you find at the deli counter is usually made from real cheese, although it may not be wholly cheese, so check the label for the words "Pasteurized Process cheese". These deli cheeses still have fewer chemicals and extracts than the individually packaged stuff, so they will usually taste fresher and more flavorful.
The Science Behind Cheese: Understanding Cow's Milk Magic
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
American cheese is a processed cheese made from a blend of several types of cheese, including cheddar, Colby, washed curd cheese, and granular cheese. It also contains sodium citrate, which allows the cheese to be pasteurised without its components separating.
American cheese is typically white or yellow/orange in colour. Yellow American cheese is seasoned and coloured with annatto.
American cheese has a mild flavour and a smooth, creamy texture. It has a medium-firm consistency and a low melting point.
American cheese is a common ingredient in classic American dishes such as cheeseburgers and grilled cheese sandwiches.