Cheddar cheese, a beloved dairy product, has a reputation for being indulgent and, unfortunately, fattening. This perception may stem from its rich, creamy texture and high-fat content, which can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess. However, understanding the factors that make cheddar cheese seem fattening is essential to appreciating its place in a balanced diet.
What You'll Learn
- Cheddar's high fat content: Each serving contains 10 grams of fat, contributing to its calorie density
- Calorie density: Cheddar's calorie density makes it easy to overeat, leading to weight gain
- Portion control: Overeating cheddar can lead to excess calorie intake, especially when consumed in large portions
- Saturated fats: Cheddar's high saturated fat content may increase cholesterol levels and promote weight gain
- Lack of fiber: Unlike some cheeses, cheddar lacks fiber, which can slow digestion and increase feelings of fullness

Cheddar's high fat content: Each serving contains 10 grams of fat, contributing to its calorie density
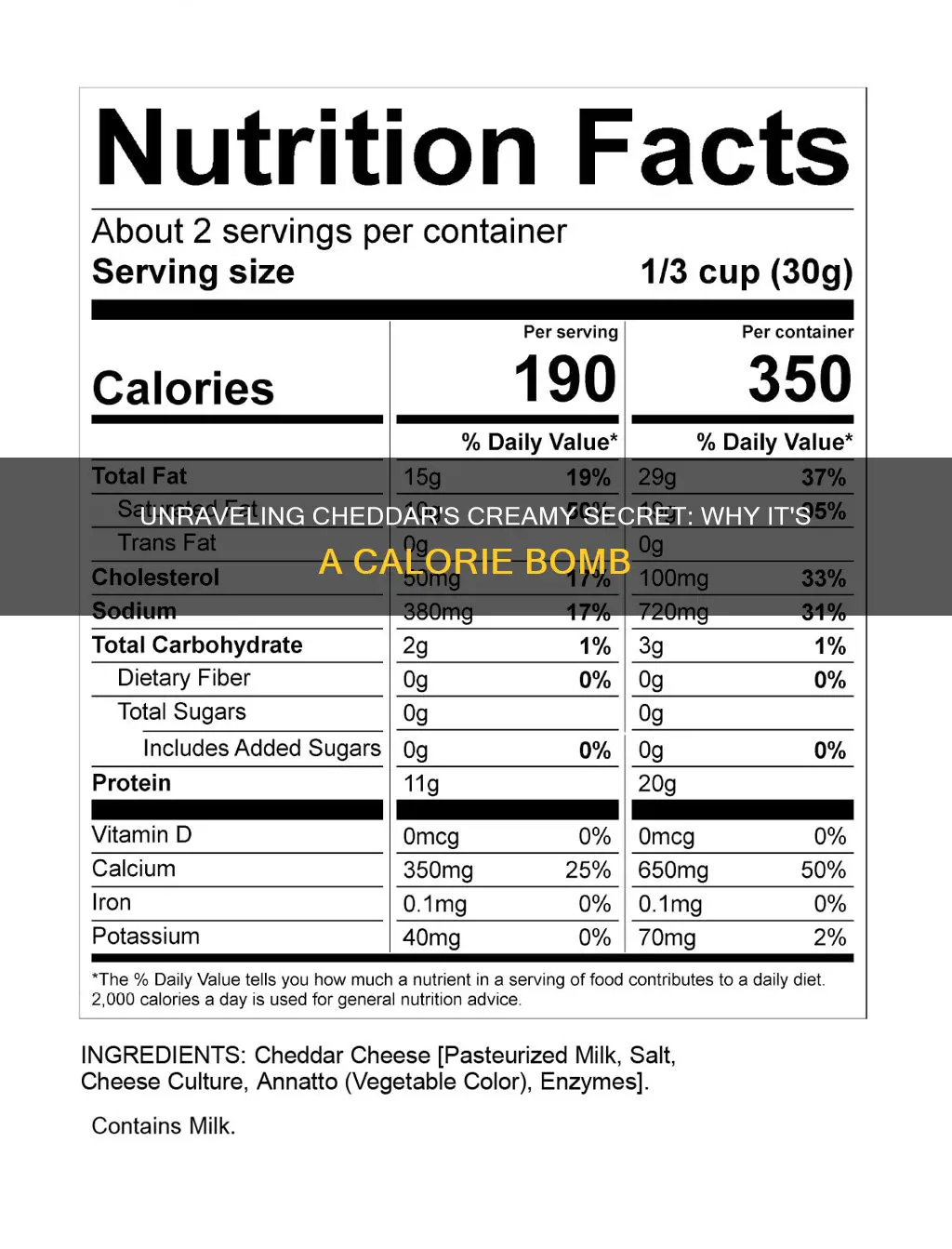
Cheddar cheese, a beloved dairy product, has gained a reputation for being a bit of a dietary villain due to its high-fat content. Each serving of cheddar, typically around 30 grams, packs a punch in terms of calories and fat. On average, a single serving of cheddar cheese contains a staggering 10 grams of fat, which is quite a significant amount, especially when compared to other cheeses. This high-fat content is a primary reason why cheddar is considered fattening.
The calorie density of cheddar is a critical factor in its classification as a high-calorie food. Calorie density refers to the number of calories in a given weight of food. In the case of cheddar, its fat content contributes to a high calorie density, meaning that a relatively small portion can provide a substantial number of calories. For instance, a 30-gram serving of cheddar contains approximately 150 calories, with a significant portion of those calories coming from the fat. This high calorie density can be a concern for those watching their weight, as it may lead to excessive calorie intake if consumed in larger quantities.
The impact of cheddar's fat content on its overall fattening nature is twofold. Firstly, the high fat content directly contributes to the calorie density, making it a dense source of energy. Secondly, fat is a more concentrated source of calories compared to carbohydrates or proteins. This means that a small amount of fat can provide a significant number of calories, making it easier to exceed daily calorie limits, especially if cheddar is consumed regularly in large portions.
Understanding the nutritional profile of cheddar is essential for those seeking to manage their weight or maintain a healthy diet. While cheddar offers some protein and essential nutrients, its high-fat content and calorie density make it a food to be consumed in moderation. For those who enjoy cheddar, incorporating it into a balanced diet and being mindful of portion sizes can help mitigate the potential negative effects of its high-fat content.
In summary, the high-fat content of cheddar cheese, with each serving containing 10 grams of fat, contributes to its calorie density and overall fattening nature. This makes cheddar a food that should be enjoyed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Awareness of its nutritional profile can help individuals make informed choices about their food intake and overall health.
Mature Cheddar's Fat Content: Unveiling the Creamy Truth
You may want to see also

Calorie density: Cheddar's calorie density makes it easy to overeat, leading to weight gain
Cheddar cheese, a beloved dairy product, has a unique characteristic that often contributes to its reputation as a fattening food: its calorie density. Calorie density refers to the number of calories contained in a given volume or weight of a food. When it comes to cheddar, this density can be surprisingly high, especially compared to other cheeses. This high calorie density is a result of the cheese's composition and the process of making it. Cheddar is primarily made from milk, and the transformation from milk to cheese involves the addition of bacteria and enzymes that break down lactose (milk sugar) and proteins, creating a concentrated source of energy.
The high calorie density of cheddar means that each bite provides a significant amount of energy. For example, a 100-gram serving of cheddar cheese contains approximately 400 calories. This is notably higher than the same weight of many other cheeses, such as mozzarella or Swiss cheese, which typically have around 200-250 calories per 100 grams. The difference in calorie density is further emphasized when comparing cheddar to fresh produce, which generally has a much lower calorie density, making it easier to consume larger portions without excessive calorie intake.
This high calorie density in cheddar cheese can have a significant impact on weight management. When you eat a food with high calorie density, you're more likely to consume a larger volume of it, as the calories are spread out over a substantial amount of food. As a result, it's easier to overeat cheddar compared to other, less dense foods. For instance, a single serving of cheddar cheese might be a small piece, but due to its calorie density, it can quickly add up in terms of calories, especially if consumed in excess.
The consequence of this high calorie density is often weight gain. Overeating cheddar cheese can lead to an excess of calorie intake, which, when not balanced by physical activity, results in an energy surplus. Over time, this surplus can contribute to an increase in body weight. Additionally, the high fat content in cheddar, which is a significant contributor to its calorie density, can further exacerbate weight gain, as fat is a highly calorie-dense macronutrient.
Understanding the concept of calorie density and its impact on cheddar cheese consumption can be a valuable tool for those aiming to manage their weight. By being mindful of portion sizes and the calorie density of foods like cheddar, individuals can make informed choices to ensure their dietary habits align with their health and weight goals. It's a reminder that while cheddar cheese can be a delicious and nutritious part of a balanced diet, moderation and awareness of its unique characteristics are key to enjoying it without the extra pounds.
Where to Find Bandon Cheddar in Phoenix: A Guide to Local Stores
You may want to see also

Portion control: Overeating cheddar can lead to excess calorie intake, especially when consumed in large portions
Cheddar cheese, a beloved staple in many cuisines, is often associated with indulgence and comfort. However, its creamy texture and rich flavor can make it easy to overeat, leading to an excess of calorie intake. Portion control is a critical aspect of managing one's weight and overall health, especially when it comes to foods that are high in fat and calories.
The key to enjoying cheddar cheese without the guilt lies in understanding and practicing portion control. Cheddar is a dairy product that is high in fat and calories, with a single serving of cheddar cheese (about 1 ounce) containing approximately 115 calories and 9 grams of fat. While this may not seem like a significant amount, it can quickly add up when consumed in larger portions. For instance, a single slice of cheddar cheese on a sandwich or a small handful of cheddar cubes can easily exceed the recommended serving size, leading to an unintended calorie surplus.
To avoid overeating cheddar, it's essential to be mindful of portion sizes. A good rule of thumb is to stick to the recommended serving size, which is typically around 1-2 ounces of cheese per meal. This can be achieved by using measuring cups or a food scale to accurately portion out the cheese. Additionally, paying attention to the visual cues of a standard serving size can be helpful. A single slice of cheese, about the size of a credit card, or a small handful of cheese cubes, should be considered a standard portion.
Another strategy to practice portion control with cheddar is to pair it with other foods that are lower in calories. For example, adding cheddar to a salad or sandwich can help balance the calorie content of the meal. Alternatively, using cheddar as a topping or ingredient in recipes can allow for better portion control, as it can be incorporated into a larger dish. This way, the overall calorie content of the meal can be more easily managed.
In conclusion, while cheddar cheese is a delicious and versatile food, its high-calorie and high-fat content make portion control essential. By being mindful of serving sizes and incorporating cheddar into balanced meals, individuals can enjoy this tasty cheese without compromising their health goals. Remember, moderation and awareness are key to making cheddar cheese a part of a healthy and enjoyable diet.
The Smelly Secret: Why Cheddar Cheese Stinks
You may want to see also

Saturated fats: Cheddar's high saturated fat content may increase cholesterol levels and promote weight gain
Cheddar cheese, a beloved dairy product, has a reputation for being a bit of a dietary villain, especially when it comes to weight gain and cholesterol levels. One of the primary reasons for this reputation is the high saturated fat content found in cheddar. Saturated fats are a type of fat that is known to have a significant impact on our health, particularly in relation to cholesterol and weight management.
Saturated fats, as the name suggests, have a high degree of saturation, meaning they contain no double bonds in their fatty acid chains. This structural characteristic makes them more stable and less prone to spoilage, which is why they are commonly used in processed foods and have a longer shelf life. However, this stability comes at a cost to our health. When we consume saturated fats, they can raise our low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels, often referred to as 'bad' cholesterol. High LDL cholesterol is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, as it can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the chances of heart attacks and strokes.
The relationship between saturated fats and cholesterol is well-documented. Numerous studies have shown that a diet high in saturated fats can significantly increase LDL cholesterol levels. Cheddar cheese, being a dairy product, naturally contains a substantial amount of saturated fats, which can contribute to this increase. For instance, a 100-gram serving of cheddar cheese can provide around 30 grams of fat, with a significant portion of it being saturated. This high saturated fat content can lead to a rapid rise in blood cholesterol levels, especially in individuals who are genetically predisposed to high cholesterol or those who already have elevated cholesterol levels.
Moreover, the impact of saturated fats on weight gain is another critical aspect to consider. Saturated fats are calorie-dense, providing approximately 9 calories per gram, which is higher than the 4 calories per gram provided by carbohydrates and proteins. When we consume foods high in saturated fats, we are more likely to take in excess calories, which can lead to weight gain over time. Cheddar cheese, with its rich flavor and creamy texture, is often used as a topping or ingredient in various dishes, adding a significant number of calories to the meal. This can be particularly problematic when consumed in large quantities or as part of an unbalanced diet.
In summary, the high saturated fat content in cheddar cheese is a significant contributor to its reputation as a fattening food. This type of fat can increase LDL cholesterol levels, a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and its calorie-dense nature can lead to weight gain. While cheddar cheese can be a delicious and nutritious part of a balanced diet, it is essential to be mindful of portion sizes and consider the overall dietary context to ensure a healthy lifestyle.
Unveiling the Secret: Is Rennet in Cheddar Cheese?
You may want to see also

Lack of fiber: Unlike some cheeses, cheddar lacks fiber, which can slow digestion and increase feelings of fullness
Cheddar cheese, a popular and beloved dairy product, has often been associated with a higher calorie content and, consequently, weight gain. One of the primary reasons for this perception is the cheese's lack of fiber. Unlike some other food groups, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, cheddar cheese is relatively low in dietary fiber. Fiber plays a crucial role in digestion and can significantly impact one's overall calorie intake. When consumed, fiber adds bulk to the digestive system, which slows down the process of digestion. This slow digestion can lead to a prolonged feeling of fullness, reducing the urge to eat more frequently. As a result, individuals may feel satisfied with smaller portions, potentially preventing excessive calorie consumption.
In the case of cheddar, its smooth and creamy texture, coupled with a high fat content, can make it a less satiating food compared to fiber-rich options. The absence of fiber means that cheddar cheese is quickly digested and absorbed, providing a rapid energy boost without the prolonged feeling of satisfaction. This can lead to a cycle of overeating, as individuals may find themselves craving more cheese or other high-calorie foods shortly after consumption.
The impact of fiber on weight management is well-documented. Studies have shown that a diet rich in fiber can promote weight loss and help maintain a healthy weight. Fiber's ability to slow digestion and regulate blood sugar levels can also prevent spikes in insulin, which is crucial for weight control. By contrast, a diet low in fiber may contribute to rapid weight gain, especially when combined with a high-fat diet like that of cheddar cheese.
To make cheddar cheese more satisfying and potentially less fattening, consider incorporating it into meals with high-fiber ingredients. For example, adding cheddar to a salad with leafy greens, tomatoes, and whole-grain bread can increase the fiber content of the meal, making it more filling. Alternatively, pairing cheddar with fruits or vegetables can also provide a more balanced nutritional profile.
In summary, the lack of fiber in cheddar cheese is a significant factor in its perceived fattening nature. By understanding this aspect of nutrition, individuals can make informed choices to include cheddar in a healthier diet or opt for fiber-rich alternatives to manage their weight effectively.
Where to Find Kraft American and Cheddar Shredded Cheese: A Store Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Cheddar cheese, while delicious, is relatively high in fat and calories. A 100-gram serving of cheddar cheese contains approximately 36 grams of fat and 110 calories. The high-fat content is primarily due to the cheese-making process, which involves curdling milk and separating the curds, which are then pressed into a solid form. This process can result in a higher fat concentration compared to other cheeses.
While cheddar cheese can be considered fattening due to its fat content, it is not inherently unhealthy. The key factor is portion control and overall dietary balance. A moderate amount of cheddar cheese can be included in a healthy diet as part of a balanced meal. However, excessive consumption, especially when paired with high-calorie condiments or excessive bread intake, may contribute to weight gain.
Yes, cheddar cheese offers several nutritional advantages. It is an excellent source of protein, providing essential amino acids for muscle growth and repair. Cheese also contains important minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin B12. Additionally, it is a good source of probiotics, which support gut health. Despite its higher fat content, cheddar cheese can be a valuable component of a nutritious diet when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.







