If you are taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), it is important to follow a low-tyramine diet to avoid a hypertensive crisis, which can lead to a stroke. Tyramine is a compound that affects your blood pressure and is usually broken down by the MAO enzyme. However, when taking MAOIs, the MAO enzyme is blocked, leading to a buildup of tyramine in the body, which can cause a rapid and severe rise in blood pressure. Aged cheeses, such as cheddar, contain high levels of tyramine and should be avoided by those taking MAOIs.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Why should you avoid cheddar cheese when taking MAOIs? | Cheddar cheese is an aged cheese that contains high levels of tyramine. When taking MAOIs, the body cannot process tyramine well, which can lead to a hypertensive crisis, a rapid and severe rise in blood pressure that can cause serious health issues. |
| Examples of aged cheeses to avoid | Fontina, Brie, Blue, Camembert, Munster, Swiss |
| Other foods to avoid | Aged meats, fermented foods, chocolate, alcohol |
| Safe cheeses | Cottage cheese, cream cheese, ricotta, part-skim mozzarella, American processed cheese |
Explore related products
$9.3 $15.99
$11.6 $19.99
What You'll Learn

MAOIs and tyramine can cause a hypertensive crisis
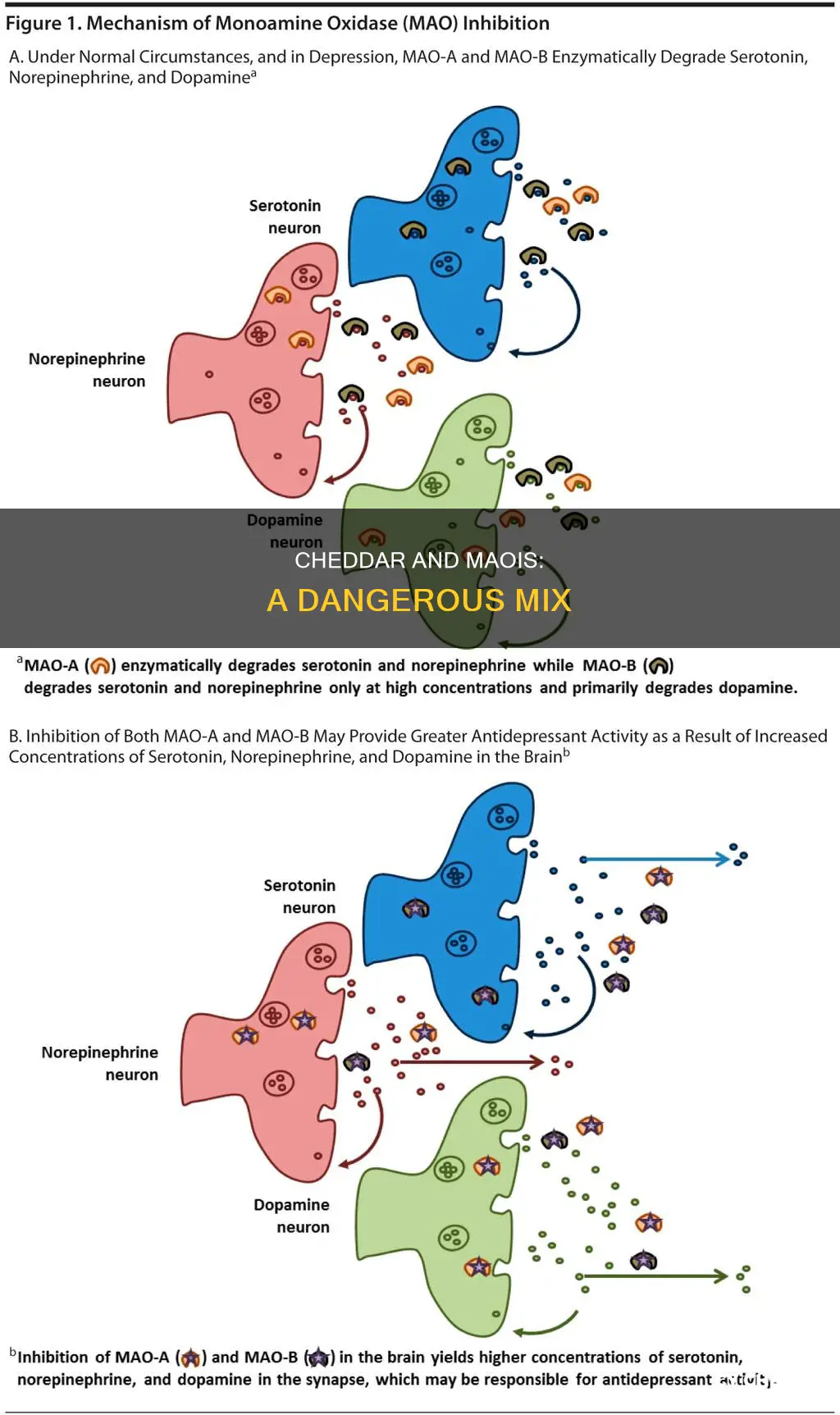
MAOIs, or monoamine oxidase inhibitors, are a class of medications that were first introduced in the 1950s to treat depression. They work by restricting the MAO enzyme, which normally breaks down tyramine, to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. However, this inhibition can lead to a dangerous buildup of tyramine in the body.
Tyramine is a compound commonly found in aged or fermented foods, and its levels in food increase during the ageing, spoiling, or decay process. When a person takes MAOIs, their body cannot process tyramine efficiently, leading to elevated levels of tyramine. This elevation in tyramine can cause a rapid and severe rise in blood pressure, resulting in a hypertensive crisis.
A hypertensive crisis is a medical emergency where blood pressure reaches dangerously high levels. It can lead to serious health issues, such as a stroke, and requires immediate medical attention. To avoid a hypertensive crisis, it is crucial for individuals taking MAOIs to follow a low-tyramine diet.
Cheddar cheese, being an aged cheese, contains high levels of tyramine. Therefore, it is recommended that individuals taking MAOIs avoid consuming cheddar cheese to prevent a hypertensive crisis. Other aged cheeses that should be avoided include fontina, brie, blue cheese, camembert, munster, and Swiss cheese. Fresh cheeses with low tyramine levels, such as cottage cheese, cream cheese, ricotta, and part-skim mozzarella, can be consumed in moderation as long as they are refrigerated properly.
In addition to cheese, other tyramine-rich foods to avoid while taking MAOIs include aged or cured meats, fermented foods, chocolate, and alcohol. It is important to carefully inspect meals and snacks to ensure they do not contain any high-tyramine ingredients. Following a low-tyramine diet is essential for individuals taking MAOIs to prevent the potentially life-threatening consequences of a hypertensive crisis.
Cheddar Cheese: Is It Harmful to Your Health?
You may want to see also

Aged cheeses are high in tyramine
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medications, your body cannot process tyramine very well. MAOIs restrict the MAO enzyme to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. However, if the MAO enzyme is inhibited, tyramine can reach dangerously high levels in your body. Elevated tyramine can cause your blood vessels to narrow, possibly leading to critically high blood pressure, also known as a hypertensive crisis.
Tyramine levels in food increase during the spoiling or decay process. Therefore, it is important to only eat fresh and freshly cooked foods while taking MAOIs. This includes avoiding leftovers, even if they have been refrigerated, and not consuming products beyond their freshness or expiration date.
It is important to note that tyramine is not only found in aged cheeses but also in other aged, cured, pickled, or smoked meats, as well as fermented foods. It is always recommended to discuss any dietary questions or concerns with a healthcare provider to ensure you have no negative reactions to MAOIs.
Moldy Cheddar: Cut or Toss?
You may want to see also

MAOIs and cheese: a history of the discovery
MAOIs, or monoamine oxidase inhibitors, were first introduced in the 1950s as one of the earliest antidepressants in the United States. They work by restricting the MAO enzyme, which helps regulate the levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine in the body. By inhibiting this enzyme, MAOIs can reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
However, inhibiting the MAO enzyme can also lead to a dangerous buildup of tyramine in the body. Tyramine is a compound found in certain foods and beverages, particularly those that are aged, fermented, or spoiled, such as cheese. As foods age or spoil, the levels of tyramine increase. This is why aged cheeses like cheddar are high in tyramine.
In the first decade of MAOI use, the dangers of combining them with tyramine-rich foods were not fully understood. Many patients were consuming cheddar cheese with their MAOI medication, but hypertensive emergencies associated with this combination were rare. It wasn't until 1963 when a psychiatric resident, Barry Blackwell, reported 12 patients who had experienced hypertensive crises apparently related to the use of MAOIs.
It took several more years for researchers to identify cheese as the culprit in these cases. They discovered that cheese, especially aged and fermented varieties, contains high levels of tyramine. When patients taking MAOIs consume tyramine, the combination can lead to a rapid and severe rise in blood pressure, known as a hypertensive crisis, which can have serious health consequences.
Kraft Cheddar and Velveeta: What's the Real Difference?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Other foods and drinks to avoid with MAOIs
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medications, your body cannot process tyramine very well. Typically, tyramine levels rise in food and beverages as they age, ferment, or are stored for long periods. As a result, MAOI diets contain little to no tyramine, which means you are avoiding foods that are high in tyramine.
- Aged cheeses: While most sources agree that aged cheeses should be avoided, some cheeses may be safe in specific servings. For example, fresh mozzarella contains little tyramine, so it appears to be safe for patients taking MAOIs.
- Other dairy products: This includes yogurt, milk, and cream.
- Aged, cured, pickled, or smoked meats: Examples include chorizo, sausage, corned beef, salami, and pepperoni.
- Alcohol: Wine, most bottled beers, and most hard liquors. Some sources recommend avoiding red wine, especially Chianti, while others state that red wine contains very low levels of tyramine.
- Chocolate: Some authorities caution that European chocolates are riskier than American chocolates, perhaps because they contain more cocoa and less milk.
- Caffeine: Caffeinated beverages should be limited to no more than two per day.
- Fermented foods: These include soy sauce and other fermented products.
- Leftovers: Even if they have been refrigerated, leftovers should be avoided.
It is important to note that the list of foods to avoid with MAOIs may change over time as researchers continue to study the tyramine content in different foods. Additionally, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for specific dietary guidelines and to ensure safe medication use.
Moldy Cheddar: Is It Safe to Eat?
You may want to see also

Safe cheeses to eat when taking MAOIs
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medications, it's important to follow a low-tyramine diet. This is because the body cannot process tyramine well when taking MAOIs, and elevated levels of tyramine can lead to dangerously high blood pressure (hypertensive crisis).
Tyramine levels in food increase as they age, ferment, or are stored for long periods. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid aged cheeses such as cheddar, fontina, brie, blue, camembert, munster, and Swiss. However, some fresh cheeses with low tyramine content are considered safe to consume, including mozzarella, American, cottage, ricotta, and cream cheese. Freshly made pizzas with mozzarella and pepperoni from reputable chains are also likely safe.
In addition to cheese, other foods to avoid when taking MAOIs include aged, cured, pickled, or smoked meats such as chorizo, sausage, corned beef, salami, and pepperoni. It is also important to practice proper food handling, preparation, and safety practices to prevent spoilage and food poisoning. Leftovers, even if refrigerated, should be avoided.
It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider for specific dietary guidelines and to discuss any medications or supplements being taken to ensure a safe and effective treatment plan while taking MAOIs.
Fat-Free Shredded Cheddar: Gluten-Free Kraft Goodness
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
MAOIs, or monoamine oxidase inhibitors, restrict the MAO enzyme to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. When taking MAOIs, the body cannot process tyramine very well, and it builds up to excessive levels in the body. Cheddar cheese is an aged cheese that contains high levels of tyramine, which can lead to dangerously high blood pressure and a hypertensive crisis.
A hypertensive crisis is a medical emergency where there is a rapid and severe rise in blood pressure. This can lead to serious health issues, such as a stroke.
Other foods high in tyramine that should be avoided when taking MAOIs include aged meats, fermented foods, chocolate, and alcohol. It is important to follow a low-tyramine diet and restrict foods with high levels of tyramine to prevent a hypertensive crisis.
Yes, some cheeses with low tyramine levels that can be eaten in moderation while taking MAOIs include cottage cheese, cream cheese, ricotta, part-skim mozzarella, and American processed cheese. However, it is important to note that these cheeses should be refrigerated for no more than two to three weeks.











































