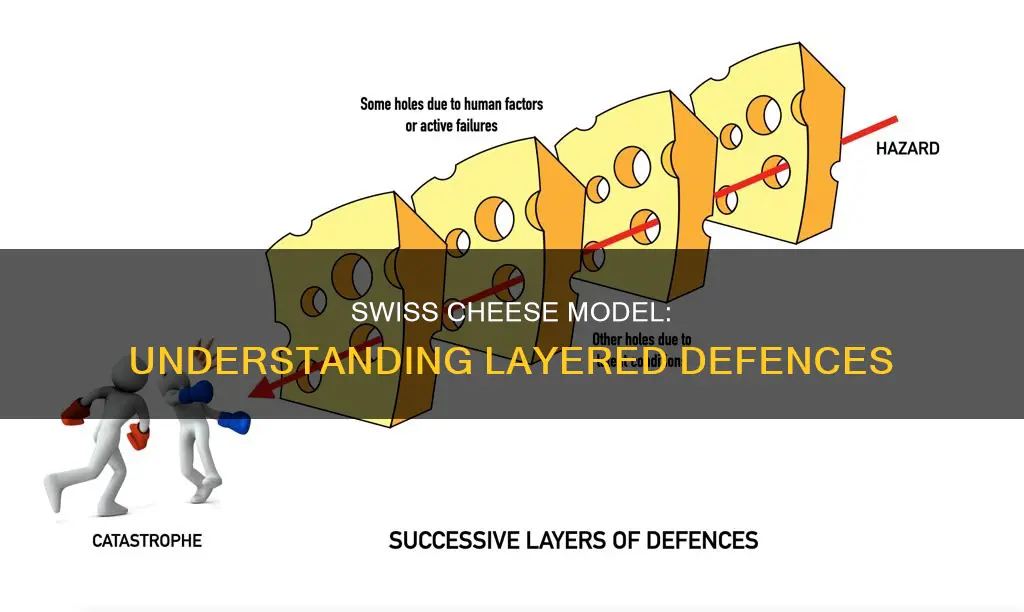
The Swiss Cheese Model is a model used in risk analysis and management. It was originally proposed by James Reason of the University of Manchester and likens human systems to multiple slices of Swiss cheese, stacked side by side. Each slice of cheese is symbolic of a given measure taken to minimize risk, with the holes in the cheese representing weaknesses in individual parts of the system. The model is used to understand why accidents occur and how they can be prevented, and has been applied in a variety of industries including healthcare, aviation, and engineering.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To understand why accidents occur despite efforts to prevent them |
| Use | Guide root cause analyses (RCAs) and safety efforts across industries including healthcare, aviation, engineering, and emergency services |
| Model | Human systems are likened to slices of Swiss cheese with holes of varying size and position |
| Holes | Represent weaknesses or potential failures in individual parts of a system |
| Slices | Represent lines of defense or barriers against accidents |
| Failure | Occurs when holes in slices align, creating a "trajectory of accident opportunity" |
| Dynamic Holes | Holes open and close, allowing the system to function without catastrophe |
| Weaknesses | Not every hole leads to an accident, and some may be inconsequential or detected and corrected |
| Root Cause | A failure cannot usually be traced back to a single root cause but is often a combination of factors |
| Latent Errors | Triggered by active errors or unsafe behaviors by individuals |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn

Identifying weak points
The Swiss Cheese Model is a model used in risk analysis and risk management. It is used to identify weak points in a system and develop strategies to address them. The model likens an organisation's defences against failure to slices of Swiss cheese, with the holes in the cheese representing weaknesses in the system.
Each slice of cheese in the model represents a different safety-critical system, and each slice has its own unique set of holes. These holes are the system's weak points, where there is potential for failure. By identifying these weak points, organisations can address them and prevent accidents from occurring.
The model demonstrates that accidents are rarely the result of a single root cause but are often caused by a combination of factors. This is because, in reality, lapses and weaknesses in one area of defence are often mitigated by other areas of defence, preventing a single point of failure. For example, a nurse who mis-programs an infusion pump may notice the error and correct it before any harm is caused.
The Swiss Cheese Model has been applied in a variety of industries, including healthcare, aviation, engineering, and emergency services. In healthcare, for example, the model has been used to understand that medical errors can be the result of system flaws rather than individual character flaws. This has led to improvements in patient safety and a better understanding of how to prevent accidents.
By using the Swiss Cheese Model to identify weak points in a system, organisations can develop strategies to address these weaknesses and improve overall safety. This might involve implementing additional safety measures, improving existing defences, or addressing latent failures that could contribute to accidents.
Gouda's Versatility: Cooking, Snacking, and More!
You may want to see also

Developing strategies
The Swiss Cheese Model is a powerful tool for developing strategies to prevent errors and manage risks in complex systems. It is widely used in various industries, including healthcare, aviation, engineering, and other fields. When applying the model, organizations can develop robust and multi-layered defence strategies by understanding that failures usually result from multiple factors aligning rather than a single root cause.
Each slice of Swiss cheese in the model represents a defensive layer in the system, such as procedures, training, or equipment. The holes in the cheese symbolise weaknesses or vulnerabilities in these defences. By identifying these weak points, organizations can develop strategies to address them and prevent failures. This systematic approach to error management fosters a culture of continuous improvement and enhances overall system resilience.
One of the key strengths of the Swiss Cheese Model is its ability to encourage a proactive approach to safety. Organizations can continuously identify and address potential vulnerabilities across all levels of their operations. This proactive mindset is crucial in industries where small mistakes can lead to significant failures, such as aviation or healthcare. By adopting this model, organizations can develop stronger ways of identifying and correcting errors, reducing the probability and impact of mistakes.
The model also highlights the importance of maintaining and improving all layers of defence. It is not enough to have multiple safety measures in place; these measures must be regularly assessed, updated, and strengthened to minimize the "holes" in each layer. This ongoing process prepares organizations for potential threats and ensures that defences remain robust while maintaining secure operations.
Furthermore, the Swiss Cheese Model can be applied to develop contingency plans and alternative sourcing strategies. By identifying potential disruptions, organizations can minimize the financial impact of supply chain interruptions and enhance their ability to respond to risks effectively. This proactive approach to risk management increases investment, customer loyalty, employee satisfaction, and regulatory support.
In conclusion, the Swiss Cheese Model is a valuable tool for developing strategies to prevent errors and manage risks. By understanding the model's implications, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement, enhance system resilience, and proactively address potential vulnerabilities. The model's ability to identify weaknesses and encourage the development of robust defence strategies contributes to its effectiveness in various industries.
The Asian Cheese Conundrum: A Cultural Curiosity
You may want to see also

Analysing medical errors
The Swiss Cheese Model is a well-known and commonly used model that guides root cause analyses (RCAs) and safety efforts across a variety of industries, including healthcare. It is a useful method for relating concepts and understanding why accidents occur despite efforts to prevent them.
The model is based on the Theory of Active and Latent Failures, which posits that accidents are often the result of a combination of factors rather than a single root cause. In the Swiss Cheese Model, an organisation's defences against failure are modelled as a series of slices of Swiss cheese, with the holes in the cheese representing weaknesses or potential failures in individual parts of the system. These holes are dynamic and vary in size and position across the slices. When the holes in each slice align, it creates a "trajectory of accident opportunity", allowing a hazard to pass through and leading to a failure.
In healthcare, the Swiss Cheese Model has been used to analyse medical errors and patient safety incidents. It has helped to shift the understanding of medical errors from being solely the result of "character flaws" such as greed, ignorance, or malice, to also recognising that system flaws can contribute to errors. For example, a latent failure could be the similar packaging and storage of two different drugs in a pharmacy, leading to the administration of the wrong drug to a patient.
The Swiss Cheese Model can be used to identify weak points in a system and develop strategies to address them. Each slice of cheese can represent a different safety-critical system or line of defence, such as management, allocation of resources, or a safety program. By identifying the holes in each slice and understanding their relationships, organisations can implement additional defences to prevent a single point of failure. This can help to maximise productivity while minimising the risk of harm.
While the Swiss Cheese Model has been widely accepted and applied, it has also faced some criticisms. Some argue that it is used too broadly and without sufficient support from other models. Additionally, there may be variations in how different individuals interpret the model, which can impact the effectiveness of promoting a shared culture of safety. Despite these criticisms, the Swiss Cheese Model remains a valuable tool for analysing medical errors and improving patient safety.
Cheese for Queso: Picking the Perfect Melt
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Understanding accidents
The Swiss Cheese Model is a theory that explains why accidents happen and how they can be prevented. It is used as a guide for root cause analyses (RCAs) and safety efforts across a variety of industries, including healthcare, engineering, and aviation. The model is based on the Theory of Active and Latent Failures, which posits that accidents are often the result of a combination of factors rather than a single root cause.
In the Swiss Cheese Model, an organisation's defences against failure are modelled as slices of Swiss cheese with holes of varying sizes and positions. The holes represent weaknesses or potential failures in the system. When the holes in each slice align, it creates a "trajectory of accident opportunity", allowing a hazard to pass through all the defences and leading to a failure. This model demonstrates that a lapse in one defence does not necessarily lead to a risk materialising, as there are other defences in place to prevent a single point of failure.
The model helps safety professionals identify and address weaknesses in each layer of the system to prevent future accidents. For example, in healthcare, a latent failure could be similar packaging and storage of two different drugs in a pharmacy, leading to the administration of the wrong drug to a patient. This understanding led to the realisation that medical errors can result from "system flaws, not character flaws", challenging the notion that individual mistakes are the sole cause of accidents.
The Swiss Cheese Model has been criticised for being too simplified and broadly applied without enough supporting models. There is also a concern that the interpretation of the model varies among different users, impacting the effectiveness of a shared culture of safety. Despite these criticisms, the model has gained widespread acceptance and is considered a useful method for understanding accidents and improving patient safety.
Provolone Cheese: Uses and Pairings
You may want to see also

Fostering continuous improvement
The Swiss Cheese Model is a simple yet effective methodology that has been widely adopted across sectors, including healthcare and aviation. It is a valuable tool for fostering continuous improvement by encouraging a systemic view of accidents and failures.
The model depicts an organisation's defences against failure as slices of Swiss cheese, with holes representing weaknesses or potential failure points in individual parts of the system. When these holes align, a failure occurs. This perspective shifts the focus from blaming individuals to understanding and improving the system as a whole. By recognising that errors are often the result of multiple factors, organisations can develop more robust and multi-layered defence strategies.
In healthcare, the Swiss Cheese Model is used to improve patient safety. Each aspect of patient care, from prescribing medication to medical procedures, can be viewed as a slice of cheese. Providers can identify weak points in the process and implement measures to reduce the chances of errors that could harm patients. For example, multiple checks on patient identification and medication dosage calculations can help detect and correct mistakes.
The aviation industry also relies heavily on the Swiss Cheese Model due to the severe consequences of failures. It guides pilot training, aircraft maintenance, and air traffic control operations, helping to ensure critical safety layers are in place. The model's ability to identify weak points and develop strategies to address them is crucial in this context.
The model's strength lies in its applicability across various industries and scenarios. It encourages a proactive approach to safety, where organisations continuously identify and address vulnerabilities. By adopting this strategic view of weaknesses and promoting continuous improvement, businesses can achieve higher standards of safety while reducing hazards.
In-N-Out's Cheese: The Secret to Their Success
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Swiss Cheese Model is a model used in risk analysis, risk management, and accident causation. It likens human systems to multiple slices of Swiss cheese, with holes representing potential failures.
Each slice of cheese represents a safety barrier or precaution. The holes in the cheese represent weaknesses or potential failure points. When the holes align, a failure occurs.
The Swiss Cheese Model has been applied in various industries, including healthcare, aviation, and engineering. For example, in healthcare, it can be used to analyse adverse events such as wrong-site surgery.
The Swiss Cheese Model helps organisations understand why accidents occur despite their best efforts to prevent them. It also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, enabling teams to refine their safety procedures and enhance overall safety.
One criticism of the Swiss Cheese Model is that it is too broad and may oversimplify how accidents occur. It is important to have a good understanding of the underlying theory to interpret the model correctly.