Cheese is a beloved food, but its impact on heart health has been a topic of debate. While cheese is a good source of calcium and protein, it is also high in saturated fat and sodium, which can increase the risk of heart disease. However, research has not found a direct link between cheese consumption and heart issues. In fact, some studies suggest that eating cheese in moderation may even be beneficial for heart health, potentially due to the fermentation process. To include cheese in a heart-healthy diet, it is recommended to opt for low-fat or reduced-fat varieties, keep portions small, and pair cheese with other nutritious foods.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Cheese's impact on heart health | Research suggests that eating a small portion of cheese every day may be beneficial for heart health. |
| Cheese's nutritional value | Cheese is a source of calcium, protein, vitamins A, B12, vitamin D, vitamin K2, and probiotics. |
| Cheese's drawbacks | Cheese can be high in saturated fat, sodium, and calories. |
| Recommended types of cheese | Mozzarella, feta, ricotta, cottage cheese, and reduced-fat cheeses are lower in fat and/or sodium. |
| Pairing cheese with other foods | Cheese can be part of a heart-healthy diet when paired with other heart-healthy foods, fruits, whole-grain crackers, or sprinkled on a salad. |
| Lifestyle changes | Improving heart health involves a combination of nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle changes, such as limiting alcohol intake and prioritizing sleep. |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn
- Cheese is high in saturated fat, which can increase the risk of heart disease
- Research suggests that eating cheese daily may be beneficial for heart health
- Low-fat cheeses, such as mozzarella, feta, and cottage cheese, are healthier options
- Cheese is a good source of calcium, vitamin D, and protein
- Sodium and saturated fat in cheese can be counteracted by beneficial microbes

Cheese is high in saturated fat, which can increase the risk of heart disease
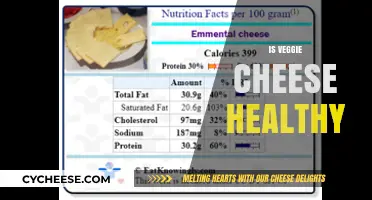
Cheese is a popular food that is often high in fat, sodium, and calories. While it can be part of a healthy diet, it is important to monitor intake and choose lower-fat varieties when possible. This is because cheese, especially full-fat varieties, can be high in saturated fat, which has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
Saturated fat is known to raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels in the body, which can, in turn, increase the risk of heart disease. As such, it is generally recommended to limit saturated fat intake to 5-6% of total daily calories or about 13 grams per day for a 2,000-calorie diet. This is especially important for those who already have heart disease or are at high risk of developing it.
While cheese can be high in saturated fat, not all cheeses are equal in this regard. For example, mozzarella, ricotta, feta, and cottage cheese are lower in fat and sodium than other varieties, making them better choices for heart health. Additionally, these cheeses can provide beneficial nutrients like protein, calcium, and vitamin K2, which are important for overall health, including heart health.
It is worth noting that the link between dairy consumption and heart disease risk is not entirely clear. Some studies have found that dairy fat is not associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease when compared to the same amount of calories from carbohydrates. Additionally, diets that include dairy products, even full-fat varieties, do not seem to raise heart disease risk and may even help reduce the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Overall, while cheese can be part of a heart-healthy diet, it is important to choose lower-fat varieties, monitor portion sizes, and pair it with other nutritious foods. This can help ensure that the benefits of cheese consumption outweigh any potential risks associated with its saturated fat content.
Cheese Spreads: Healthy or Unhealthy?
You may want to see also

Research suggests that eating cheese daily may be beneficial for heart health
Cheese is a beloved food for many, but its nutritional profile has sparked debates about its impact on health, particularly heart health. While it is well-known that cheese can be high in saturated fat and sodium, recent research suggests that eating cheese daily in moderation may offer benefits for maintaining a healthy heart.
The role of saturated fat and sodium in cheese
One of the primary concerns regarding cheese consumption is its high content of saturated fat and sodium. Saturated fat is known to increase the risk of heart disease by raising LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels. Similarly, excessive sodium intake can lead to increased blood pressure, which is a risk factor for heart disease. Therefore, it is generally recommended to opt for lower-fat cheeses, such as mozzarella, feta, cottage cheese, or reduced-fat varieties, which provide less saturated fat. Additionally, consuming cheese in moderation is essential to avoid excessive sodium and saturated fat intake.
Research insights on cheese and heart health
Despite the concerns about saturated fat and sodium, research has not found a direct link between eating cheese and developing cardiovascular diseases. In fact, some studies suggest that including cheese in your diet may have positive effects on heart health. A 2023 study indicated that a diet including cheese lowered the risk of cardiovascular disease. Another study, published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition in 2016, analyzed data from over 220,000 individuals and found that dairy fat was not associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease when compared with the same amount of calories from carbohydrates.
Cheese as a source of beneficial nutrients
Cheese also provides several essential nutrients that can contribute to overall health and heart health specifically. Cheese is a good source of calcium, which is crucial for bone health. Additionally, cheese contains vitamin K2, which helps prevent calcium buildup in the walls of arteries and veins, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease. Certain types of cheese, like mozzarella, provide probiotics that can benefit gut and immune health. Furthermore, cheese is a source of protein, and high-protein diets have been linked to weight loss and a lower risk of obesity-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease.
Incorporating cheese into a heart-healthy diet
While cheese can be part of a heart-healthy diet, it should be consumed in moderation and paired with other nutritious foods. Opting for low-fat or reduced-fat cheeses can help manage saturated fat intake. Additionally, choosing cheeses with lower sodium content, like mozzarella, can be beneficial. Enjoying a small piece of cheese as a snack with fruit or whole-grain crackers, or sprinkling it on a salad, are heart-healthy ways to include cheese in your diet.
Cheese and Fruit: Healthy Snacking
You may want to see also

Low-fat cheeses, such as mozzarella, feta, and cottage cheese, are healthier options
Cheese is a good source of calcium, protein, and vitamins A, B12, and K2. These nutrients play an important role in keeping the heart and body strong. For example, vitamin K2 helps prevent calcium from accumulating in the walls of arteries and veins, which could otherwise lead to an increased risk of blockages and heart disease.
However, cheese is also high in saturated fat and sodium, which can increase the risk of heart disease and raise LDL (bad) cholesterol. Therefore, it is recommended to consume cheese in moderation and opt for low-fat varieties when possible.
Feta, traditionally made from sheep's milk or a combination of sheep and goat's milk, is another low-fat option. It is typically lower in calories than many other cheeses, but because it is often packaged in brine to preserve freshness, it can be high in sodium. Cottage cheese is also a lower-fat option, though it contains more lactose than feta.
In addition to opting for low-fat cheeses, there are other ways to include cheese in a heart-healthy diet. Firstly, it is important to keep portions small. Instead of grating cheese onto a dish, which can be difficult to equate to a healthy portion size, it is recommended to weigh it out. Consuming cheese with fruit or whole-grain crackers, or sprinkled on a salad, is another heart-healthy way to enjoy cheese. Finally, pairing cheese with other heart-healthy foods can help ensure a balanced diet.
Cheese Puffs: Healthy or Harmful?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Cheese is a good source of calcium, vitamin D, and protein
Cheese is a beloved food for many, but its consumption should be mindful due to its potential health impacts. While cheese is a good source of calcium, vitamin D, and protein, it can also be high in saturated fat and sodium, which may negatively affect heart health. Thus, it is important to choose the right types of cheese and consume them in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Calcium
Calcium is essential for bone health, and cheese is an excellent source of this mineral. Hard cheeses, such as cheddar, provide a significant amount of calcium. For example, a 30g portion of cheddar offers over a quarter of an adult's daily calcium requirements. Other calcium-rich cheeses include mozzarella, blue cheese, and feta.
Vitamin D
Cheese also contains small amounts of vitamin D, which is crucial for calcium absorption. While lower-fat dairy products contain less vitamin D than full-fat cheese, cheese is not the best source of this nutrient. Eggs, oily fish, and fortified cereals (with low sugar) are better options for vitamin D intake.
Protein
Protein is a building block for the body, and cheese is a good source of this nutrient. Mozzarella, blue cheese, feta, and cheddar are all high in protein. A diet rich in protein can aid in weight loss, improve bone health, and lower the risk of obesity-related diseases, including cardiovascular issues.
While cheese can provide these essential nutrients, it is important to be aware of its potential drawbacks. Cheese can be high in saturated fat and sodium, which can increase the risk of heart disease and negatively impact cardiovascular health. Therefore, it is recommended to choose lower-fat cheeses, such as mozzarella, feta, cottage cheese, or reduced-fat options. Additionally, keeping portions small and weighing them out can help control intake.
Cheese Strings: Healthy or Unhealthy Snack?
You may want to see also

Sodium and saturated fat in cheese can be counteracted by beneficial microbes
Cheese is a good source of calcium, a mineral that makes up bone structure. Adults need 1,000 milligrams of calcium per day, and most hard cheeses are an excellent source. For example, one ounce of cheddar cheese has 200 milligrams of calcium (20% of the daily value). Calcium is important for heart health, as a calcium deficiency can reduce bone strength and increase the risk of osteoporosis. Cheddar is also a source of vitamin K2, which helps prevent calcium from accumulating in the walls of the arteries and veins. Inadequate vitamin K levels can cause calcium buildup, inhibiting blood flow and leading to an increased risk of blockages and heart disease.
However, cheese can be high in saturated fat and sodium, which can increase the risk of heart disease. Eating too much saturated fat can increase LDL (bad) cholesterol, which is linked to heart disease. Therefore, it is important to be mindful of the sodium and saturated fat content of cheese and to consume it in moderation. Lower-fat cheeses, such as mozzarella, feta, cottage cheese, or reduced-fat cheeses, can provide less saturated fat. Mozzarella is also lower in sodium than other cheeses.
While cheese can be high in saturated fat and sodium, it also contains beneficial microbes. Fermented dairy products like cheese may contain beneficial bacteria from the fermentation process, which can promote gut health. Additionally, some cheeses, such as mozzarella, contain probiotics that can benefit gut and immune health. These beneficial microbes may help to counteract the negative effects of sodium and saturated fat in cheese, contributing to overall heart health.
Overall, cheese can be part of a heart-healthy diet when consumed in moderation and paired with other heart-healthy foods. Research suggests that eating a small portion of cheese every day may even be beneficial for heart health. However, it is important to be mindful of the type of cheese and its sodium and saturated fat content.
Cheese and Bacon Rolls: Healthy or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Cheese is a good source of calcium and protein, and it contains vitamins A, B12, and D. However, it can be high in saturated fat and sodium, which can increase the risk of heart disease. Therefore, it is recommended to consume cheese in moderation and opt for low-fat or reduced-fat varieties.
Mozzarella is a good choice for heart health as it is lower in saturated fat and sodium compared to other cheeses. Other low-fat cheeses include feta, cottage cheese, and ricotta.
A daily serving of cheese, averaging 1.5 ounces per day, is recommended for heart health. However, it is important to keep portions small and be mindful of the sodium and saturated fat content.