Cheddar cheese is a widely consumed dairy product, known for its rich flavour and texture. It is a good source of calcium, protein, and vitamins, but it has also been associated with high levels of fat, particularly saturated fat. This has led to concerns about the potential health risks of consuming cheddar cheese, especially in relation to cardiovascular health. However, new research suggests that the impact of saturated fat in whole foods like cheese on heart health may not be as detrimental as previously believed. This has sparked debates about the pros and cons of saturated fat in dairy products, with experts calling for further investigation. In this context, the question of whether additional fat is incorporated into cheddar cheese during its production process becomes pertinent, as it could influence the overall fat content and, consequently, the nutritional profile of this popular cheese variety.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Fat Added | Yes |
| High-Fat Food | Yes |
| High-Calorie Count | Yes |
| High Saturated Fat Content | Yes |
| High Protein Content | Yes |
| High Calcium Content | Yes |
| High Vitamin K2 Content | Yes |
| High Sodium Content | Yes |
| High Phosphorus Content | Yes |
| High Zinc Content | Yes |
| High Selenium Content | Yes |
| High Riboflavin Content | Yes |
| High Vitamin A Content | Yes |
| High Vitamin D Content | Yes |
| High Lactose Content | No |
| Suitable for Lactose-Intolerant People | Yes, in small amounts |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn

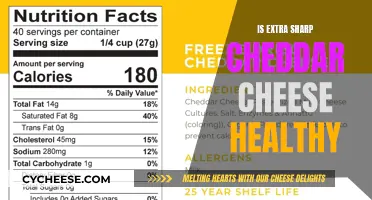
Cheddar cheese is high in fat, calories, and sodium
Cheddar cheese is a popular semi-hard cheese from England, made from cow's milk that has been matured for several months. It is a good source of calcium, with one ounce (28 grams) providing 200 mg of calcium, or 20% of the daily value. Cheddar cheese is also a source of vitamin K2, which is important for heart and bone health as it prevents calcium from building up in arteries and veins, thus reducing the risk of heart disease. In addition, cheddar cheese contains protein and other vitamins and minerals such as phosphorus, zinc, selenium, and riboflavin.
However, cheddar cheese is also high in fat, calories, and sodium. A diet high in sodium can increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. While saturated fat may not have the detrimental effects on heart health as previously believed, consuming a diet low in saturated fat is still recommended to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Cheddar cheese is high in saturated fat, with whole-milk cheddar containing 10 grams of fat and 6 grams of saturated fat per ounce.
When adding cheddar cheese to dishes, it is important to be mindful of portion sizes to avoid consuming too many calories, fat, and sodium. A generous handful of grated cheddar cheese could easily weigh 50 grams, adding more than 10% of the daily calorie requirement. To reduce calorie intake, it is recommended to use a smaller serving of vintage or mature cheddar, as these have stronger flavours and can provide the same taste with fewer calories.
While cheddar cheese is high in fat, calories, and sodium, it can still be enjoyed in moderation as part of a healthy diet. There are also alternatives to cheddar cheese, such as fat-free cheese or cheese made from almonds or cashews, for those who are concerned about their fat intake or lactose intolerant.
Edam and Cheddar: Similarities and Differences in Taste and Texture
You may want to see also

It is also a good source of protein, calcium, and vitamins
Cheddar cheese is a good source of protein, calcium, and vitamins. In terms of protein, one ounce (28 grams) of cheddar cheese offers 6.6-7 grams, which accounts for more than 30% of its calories. This can significantly add to your daily protein intake and help with muscle building and the production of enzymes.
Cheddar cheese is also rich in calcium, providing 200 mg per ounce, which meets 20% of your daily value. Calcium is critical for bone health, as it helps to prevent osteoporosis and maintain bone density.
Additionally, cheddar cheese contains vitamin K2, which is important for preventing calcium buildup in your arteries and veins, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease. Cheddar cheese also provides 10% of your daily vitamin A recommendation and 14% of phosphorus per ounce, along with smaller amounts of zinc, selenium, and riboflavin.
While cheddar cheese has nutritional benefits, it is also high in fat, particularly saturated fat, with 10 grams of total fat and 6 grams of saturated fat per ounce. Therefore, it should be enjoyed in moderation as part of a healthy diet.
Cheddar Cheese: Safe to Leave Out or Not?
You may want to see also

Whole-milk cheddar is high in saturated fat
Cheddar cheese is a delicious addition to many comfort foods. However, it is also a high-fat food, and like all such foods, it should be enjoyed in moderation. Whole-milk cheddar is high in total fat, with 10 grams per ounce, and saturated fat, with 6 grams per ounce.
Nutrition advice has traditionally recommended consuming a diet low in saturated fat to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. A high intake of saturated fat can increase the risk of diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular problems. However, new research suggests that saturated fat in whole foods such as cheese may not have the detrimental effects on heart health as previously believed. More research is needed to determine the pros and cons of saturated fat in dairy.
Cheddar cheese is also a good source of protein, with 6.6 grams per ounce, and calcium, with 200 milligrams per ounce. It is also a source of vitamin K2, which is important for heart and bone health as it prevents calcium from being deposited on the walls of arteries and veins. Cheddar also has quite a few other nutritional benefits. In addition to vitamin K2, it contains vitamin A, phosphorus, and small amounts of zinc, selenium, and riboflavin.
While cheddar cheese can be enjoyed as part of a healthy diet, it is important to be mindful of portion sizes. A generous handful of cheddar could easily weigh 50 grams, adding more than 10% of your daily calorie requirement. To enjoy the taste of cheddar while avoiding excess calories, opt for a smaller serving of a vintage or mature cheddar.
Cheddar Cheese Slices: Healthy or Unhealthy Indulgence?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Cheddar is a semi-hard cheese made from cow's milk
Cheddar cheese is known for its rich flavour and creamy texture. It is often used in dishes such as grilled cheese sandwiches, macaroni and cheese, and cheese plates. Cheddar is also a good source of protein and calcium. An ounce of cheddar cheese contains about 200 mg of calcium, which is around 20% of the daily recommended value. It also contains other essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin A, phosphorus, zinc, selenium, and riboflavin.
However, cheddar cheese also has a high-calorie count and is high in saturated fat and sodium. An ounce of cheddar cheese contains about 10 grams of total fat and 6 grams of saturated fat. While it is a delicious addition to many comfort foods, it should be enjoyed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
There are concerns about the potential health risks associated with consuming too much saturated fat. High intake of saturated fat has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular problems, diabetes, and obesity. However, recent research suggests that saturated fat from whole foods like cheese may not have the same detrimental effects on heart health as previously believed. More research is needed to fully understand the impact of saturated fat in dairy products.
Cheddar Cheese and Fatty Liver: A Safe Snack?
You may want to see also

It is one of the most popular cheeses
Cheddar cheese is one of the most popular varieties of cheese, with its origins in England. It is made from cow's milk, which is matured for several months, resulting in a semi-hard texture. The flavour of cheddar ranges from mild to extra sharp, depending on the variety. While it is a tasty addition to many dishes, its popularity is also due to its rich nutritional content.
Cheddar cheese is an excellent source of protein and calcium. A 28-gram serving of cheddar cheese contains around 6.6 grams of protein and 200 milligrams of calcium, which is about 20% of the daily recommended value. Calcium is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth, and cheddar's high calcium content contributes to its popularity.
In addition to calcium, cheddar cheese is a good source of other vitamins and minerals, including vitamin K2, vitamin A, phosphorus, zinc, selenium, and riboflavin. Vitamin K2, in particular, is important for heart health as it helps prevent calcium buildup in arteries and veins, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease.
However, despite its nutritional benefits, cheddar cheese also has some drawbacks. It is high in saturated fat, with 6 grams per ounce, and can also be high in sodium, with 190 milligrams per ounce. Excessive consumption of saturated fat and sodium can lead to increased health risks, including cardiovascular problems, obesity, and high blood pressure.
Therefore, while cheddar cheese is indeed one of the most popular cheeses, it is recommended to consume it in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Cheddar Cheese: The Art of Ripening Perfection
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, fat is naturally present in cheddar cheese. Cheddar is a semi-hard cheese made from cow's milk that has been matured for several months. It is high in fat, with 10 grams of total fat per ounce, of which six grams are saturated fat.
Yes, cheddar cheese is high in fat, with 10 grams of total fat per ounce, of which six grams are saturated fat. However, it also has several nutritional benefits, including being a good source of protein, calcium, vitamin K2, and other vitamins and minerals.
While cheddar cheese is high in saturated fat, which has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular problems, new research suggests that saturated fat from whole foods such as cheese may not have as detrimental an effect on heart health as previously believed. More research is needed to determine the pros and cons of saturated fat in dairy.
Cheddar cheese and American cheese are among the highest in cholesterol and saturated fat. In contrast, low-fat or fat-free cheeses, such as ricotta, cottage cheese, and reduced-fat cheddar, have much lower saturated fat content.
Yes, there are several alternatives to cheddar cheese for those concerned about fat intake. Reduced-fat cheddar cheese is available, and it can be used in cooking and baking. Other low-fat or fat-free cheeses are also widely available in supermarkets. For those who are lactose intolerant, cheese made from almonds or cashews can be a good alternative, although it may contain added salt.