Lactose intolerance is a common digestive condition that affects around 65% of the world's population. It occurs when the body lacks the enzyme lactase, which breaks down the lactose in dairy products. Lactose is a sugar found in milk and other dairy products, and it can cause uncomfortable symptoms such as bloating, gas, and stomach pain in people with lactose intolerance. However, not all dairy foods are high in lactose, and some cheeses are naturally low in lactose or even lactose-free. For example, hard cheeses like cheddar, Swiss, and Parmesan are often very low in lactose, while softer, creamier cheeses like ricotta and cottage cheese tend to have higher lactose content. So, is there a lot of lactose in cheddar cheese spread?
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Lactose in cheddar cheese | Trace amounts |
| Lactose in cheese spread | High |
| Cheddar cheese suitable for lactose intolerant people | Yes |
| Cheese spread suitable for lactose intolerant people | No |
Explore related products
$8.99 $9.99
What You'll Learn
- Cheddar cheese spread is higher in lactose than a block of cheddar
- Lactose intolerance affects a large percentage of the global population
- Lactose intolerance is caused by a lack of the enzyme lactase
- Hard, mature cheeses have very little lactose
- Lactose is a sugar found in milk and other dairy products

Cheddar cheese spread is higher in lactose than a block of cheddar
Lactose is a sugar found in dairy products that can be difficult for some people to digest, especially those with lactose intolerance. While cheese is generally considered to be high in lactose, not all cheeses have a lot of lactose in them. The amount of lactose in cheese varies depending on the type of cheese, the cheesemaking process, and the length of time it has been aged.
Cheddar cheese, for example, is a type of hard cheese that is often recommended as a low-lactose option. Aged cheeses, such as cheddar, have lower levels of lactose because the bacteria in the cheese break down the lactose over time, converting it into lactic acid. This means that the longer a cheese is aged, the less lactose it will contain.
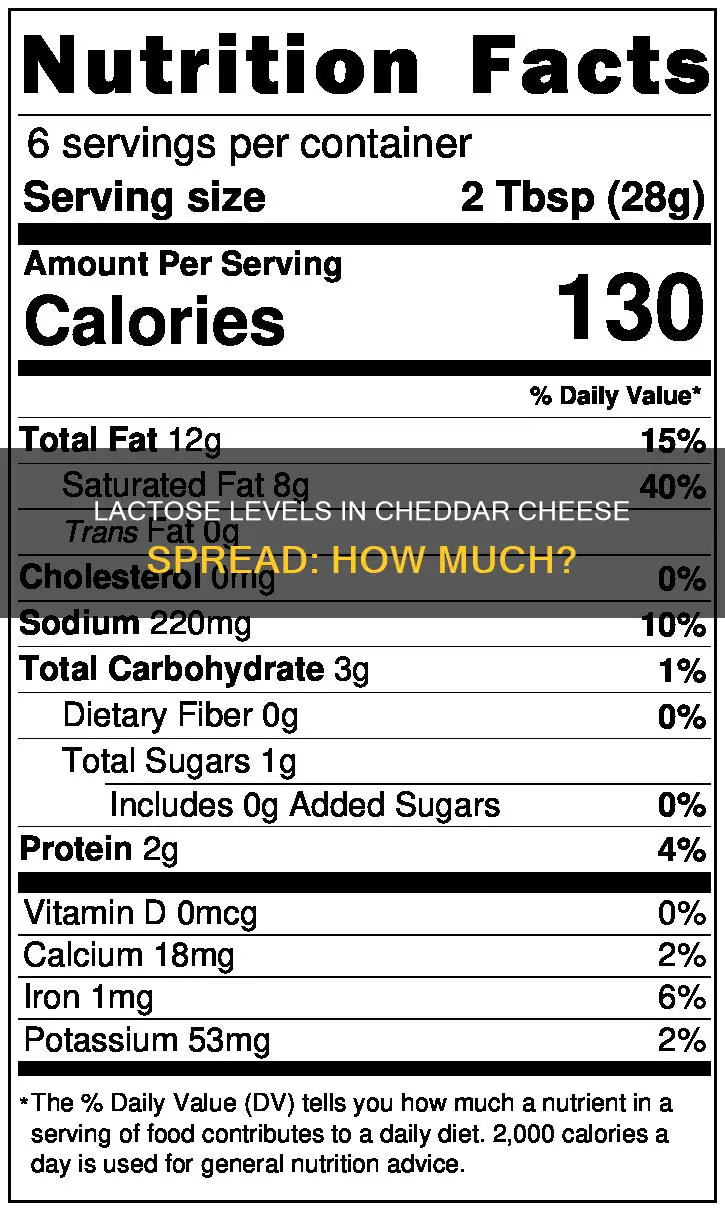
However, when it comes to cheddar cheese spread, the story is a little different. Cheese spreads tend to be higher in lactose than harder, aged cheeses like a block of cheddar. This is because cheese spreads are typically made with softer cheeses that have not been aged for as long, resulting in higher levels of lactose.
Additionally, the process of making cheese spread may also contribute to its higher lactose content. Cheese spreads are often made with a combination of cheeses and other ingredients, such as cream, which can increase the overall lactose content of the final product.
So, while a block of cheddar cheese may be a good option for those looking to reduce their lactose intake, cheddar cheese spread is likely to be higher in lactose and may not be as well-tolerated by those with lactose intolerance. It's always important to check the labels and choose cheeses that have been aged for longer if you're looking for lower-lactose options.
American or Cheddar: What's Cooper Sharp's Cheese Identity?
You may want to see also

Lactose intolerance affects a large percentage of the global population
Lactose intolerance is a common digestive condition affecting a significant portion of the global population. It is characterized by the inability to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and other dairy products. While it is not an allergy, it can cause uncomfortable symptoms such as bloating, gas, cramping, and stomach pain. The severity of these symptoms can vary among individuals.
The global prevalence of lactose intolerance is estimated to be around 65% to 68%, with higher rates in certain regions. In Asia and Africa, most people exhibit lactose malabsorption, which can lead to intolerance. In East Asian countries, the prevalence is particularly high, with rates ranging from 70% to 100%. In South America, approximately 50% of the population is lactose intolerant, and in the United States, estimates range from 15% to 36%, depending on ethnic background.
The condition is less common in Northern and Central Europe, with rates as low as 5% in some regions. This variation is due to genetic differences that have evolved over time. Northern Europeans, for example, have historically relied on livestock farming and dairy products, so those who could digest lactose had a survival advantage. As a result, the ability to produce the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose, became more prevalent in these populations.
Lactose intolerance can develop at any age, even if an individual has previously tolerated dairy without issue. It is caused by a decrease in the production of lactase, which is needed to digest lactose. This decrease can occur gradually with age or due to changes in the LCT gene.
The impact of lactose intolerance goes beyond digestive discomfort. Those affected may struggle to meet their nutritional needs, particularly for calcium and vitamin D. This can increase the risk of osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones. However, with proper dietary adjustments, individuals with lactose intolerance can ensure they receive adequate nutrition while managing their symptoms.
Cheddar Cheese: Paleo-Friendly or Not?
You may want to see also

Lactose intolerance is caused by a lack of the enzyme lactase
Lactose is a sugar found in milk and other dairy products. Lactose intolerance is a condition that makes it difficult for people to digest this sugar. It occurs when the body does not produce enough of the enzyme lactase, which is essential for breaking down lactose. Lactose intolerance can develop due to a combination of genetic and non-genetic factors.
Genetically, lactose intolerance is influenced by variants in the regulatory element within the MCM6 gene, which is inherited from parents. Individuals who do not inherit the variants that promote continued lactase production will have some degree of lactose intolerance, known as lactase non-persistence. This condition is characterised by a gradual decrease in lactase production after infancy.
Non-genetic factors that contribute to lactose intolerance include injury, surgery, infections, or chronic diseases that damage the cells producing lactase. This can lead to secondary lactose intolerance, which may not be permanent. The prevalence of lactose intolerance is lower in populations with a historical dependence on unfermented milk as a significant food source, such as those of Northern European descent.
Lactose intolerance affects a significant portion of the global population, with estimates ranging from 36% in the United States to over 65% worldwide. People with lactose intolerance may experience uncomfortable symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, gas, nausea, and diarrhea after consuming lactose-containing dairy products. However, the severity of symptoms can vary depending on the amount of lactose consumed and the individual's lactase production.
Cheese, including cheddar cheese spread, can be a part of a low-lactose diet. The cheesemaking process involves removing most of the lactose along with the water and whey. Aged cheeses, like cheddar, tend to have lower lactose levels as the bacteria present break down the remaining lactose over time. Hard cheeses, such as cheddar, are considered virtually lactose-free, making them a suitable option for individuals with lactose intolerance.
Mature Cheddar Cheese: Always Gluten-Free?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Hard, mature cheeses have very little lactose
Lactose is a type of sugar found in dairy products that can be difficult for some people to digest, especially those with lactose intolerance. While cheese is made from milk, the cheesemaking process removes a lot of the lactose. The lactose content of cheese also depends on the type of cheese and how long it has been aged.
In addition, the longer a cheese is aged, the more time bacteria have to break down the remaining lactose, further lowering its content. So, aged hard cheeses are especially low in lactose. For example, cheddar cheese, a hard cheese that is often aged, contains only trace amounts of lactose. Other examples of hard, mature cheeses with very little lactose include Swiss, Parmesan, and Pepper Jack.
People with lactose intolerance can often tolerate moderate portions of these low-lactose cheeses without experiencing uncomfortable symptoms. However, it is important to note that the severity of lactose intolerance varies from person to person, and some individuals may need to avoid all dairy products.
Cheddar Cheese: Fattening or Healthy Indulgence?
You may want to see also

Lactose is a sugar found in milk and other dairy products
Hard and mature cheeses, such as cheddar, Swiss, and Parmesan, are good options for people with lactose intolerance as they contain very little lactose. This is because, during the cheesemaking process, about 90% of the lactose in milk is removed along with the water and whey. The remaining lactose is then fermented into lactic acid by bacteria in the cheese, further reducing its lactose content. As a result, aged hard cheeses are often very low in lactose and can be tolerated by people with lactose intolerance.
However, not all cheeses are equal when it comes to lactose content. Soft, fresh, and processed cheeses, such as cottage cheese, ricotta, cream cheese, and cheese spreads, tend to have significantly higher lactose levels than hard cheeses. This is because they are higher in moisture, and in the case of processed cheeses, the manufacturing processes involved can affect the lactose content. That being said, even some higher-lactose cheeses might not cause symptoms in small portions, and individuals with lactose intolerance can often tolerate moderate amounts of lactose when consumed in moderation.
Yogurt is another dairy product that is typically well-tolerated by people with lactose intolerance. This is because yogurt contains helpful bacteria that break down lactose, reducing the amount that needs to be processed by the body. The lactose content in yogurt also decreases over time, even when stored in the fridge, as the bacteria use lactose for energy.
Pregnancy and Cheese: Is Sargento Cheddar Safe?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, there is not a lot of lactose in cheddar cheese spread. Cheddar is a hard cheese that is aged, and the longer a cheese is aged, the more lactose is broken down. Cheddar contains only trace amounts of lactose.
Other cheeses that are low in lactose include Parmesan, Swiss, Manchego, and Gruyère. Hard and mature cheeses tend to have very little lactose.
Soft cheeses like Brie, Camembert, and Mozzarella tend to have higher levels of lactose. However, even some higher-lactose cheeses might not cause symptoms in small portions.










































